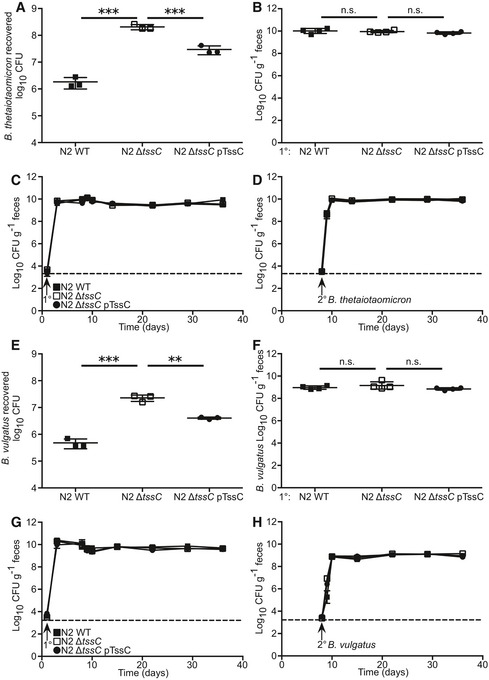
-
A
B. thetaiotaomicron recovered after in vitro competition (n = 3 competitions) with N2 WT, N2 ΔtssC, or N2 ΔtssC pTssC.
-
B–D
SPF mice (n = 4) were sequentially colonized with N2 WT, N2 ΔtssC, or N2 ΔtssC pTssC strains, followed by secondary challenge of B. thetaiotaomicron 1 week after primary colonization. Four weeks post‐secondary challenge, fecal CFU was determined for B. thetaiotaomicron (B). Fecal CFU for primary (C) and secondary strains (D) were determined for 4 weeks post‐secondary challenge.
-
E
B. vulgatus recovered after in vitro competition with N2 WT, N2 ΔtssC, or N2 ΔtssC pTssC.
-
F–H
SPF mice (n = 4) were sequentially colonized with N2 WT, N2 ΔtssC, or N2 ΔtssC pTssC followed by secondary challenge with B. vulgatus 1 week after primary colonization. Four weeks post‐secondary challenge, fecal CFU was determined for B. vulgatus (F). Fecal CFU for primary (G) and secondary strains (H) were determined for 4 weeks post‐secondary challenge.
Data information: Results are representative of three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (C, D, G, and H) or mean ± SD (A, B, E, and F). Limit of detection is denoted by a dashed line. n.s., not significant; **
P < 0.01, ***
P < 0.001. Statistical significance was determined by one‐way ANOVA, Tukey's multiple comparisons test (A, B, E, and F).