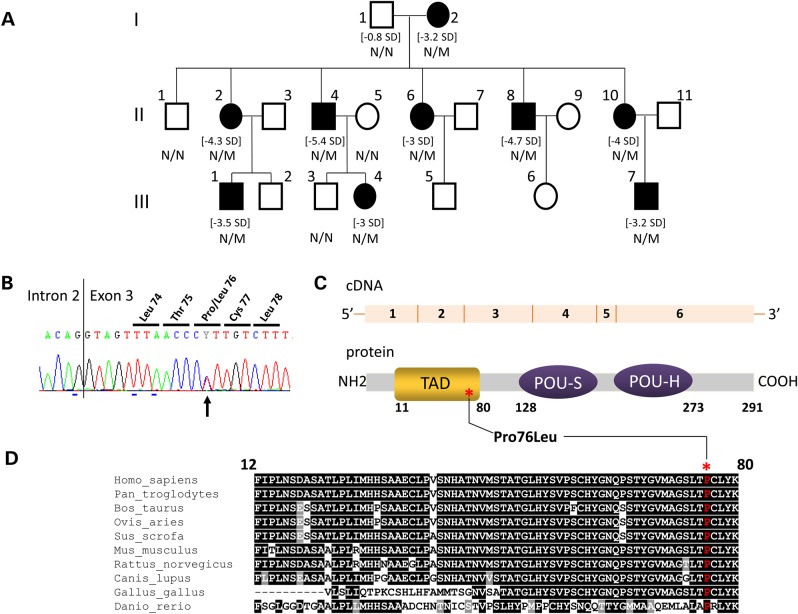
Figure 1.
Identification of a POU1F1 mutation segregating with a short stature phenotype and low serum GH levels in a three generation kindred. (A) Genealogical tree of the IGHD family. Squares: males; circles: females; filled black symbols: IGHD patients. For subjects with growth retardation, their height SD is indicated between brackets. The genotype (N/N: normal, N/M: heterozygous) is indicated under each tested individual. (B) Electrophoregram of the portion of Exon 3 showing (black arrow) the heterozygous c.227C > T transition leading to p.Pro76Leu mutation. The vertical line represents the intron–exon junction. (C) A schematic representation of the POU1F1 cDNA and POU1F1 protein: six exons encoding the 291 amino acids protein consisting of two main domains, the TAD (orange) in which the variation has been identified (noted with an asterisk) and the POU-S and POU-H domains (homeodomain, purple). (D) Evolutionary conservation of proline 76 (noted above with an asterisk): interspecies similarity (shown in one-letter code) of the TAD domain of POU1F1 aligned with sequences of the TAD domain found in nine other vertebrates species: black underlined, total conservation; gray underlined, conservative amino acid substitutions; not underlined, amino acid not conserved and indexed in a different group.