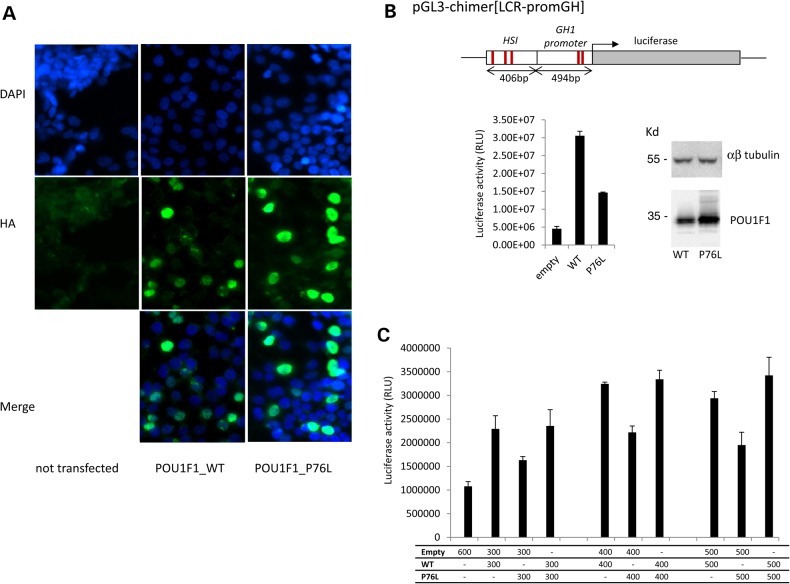
Figure 2.
Conserved nuclear localization and diminished transcriptional activity of the mutant POU1F1 protein. (A) Subcellular localization of POU1F1_WT and POU1F1_P76L in HEK293T cells transfected with the corresponding HA-tagged expression plasmids. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were immunostained with mouse anti-HA antibody (1/1000) then Alexa488 (goat anti-mouse 1/2000). Nuclei are stained in blue by DAPI. The two proteins (WT and mutated) were both localized in the nucleus. A control with no transfected cells is also shown. (B) Impact of the Pro76Leu mutation on the transcriptional capability of POU1F1. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with pcDNA3-POU1F1_WT-HA or pcDNA3-POU1F1_P76L-HA in combination with a luciferase reporter ORF under control of the HSI enhancer segment of the hGH LCR linked directly to the intact hGH promoter pGL3-chimer[LCR-promGH]. The previously defined POU1F1-binding sites in HSI and in the hGH promoter are indicated by the red lines. POU1F1 protein expression from the expression vectors was monitored by western blot with anti-POU1F1 polyclonal antibody relative to αβ-tubulin level (top). Luciferase activity represents the means ± SD of triplicate assays; a representative experiment of three experiments. (C) The assessment of a potential dominant-negative effect of the P76L mutation over the WT protein. Co-transfection of the HSI/hGH/Luc reporter with the POU1F1_WT plasmid, POU1F1_P76L plasmid in increasing amounts up to a saturation response or with a 1:1 mixture of the two plasmids.