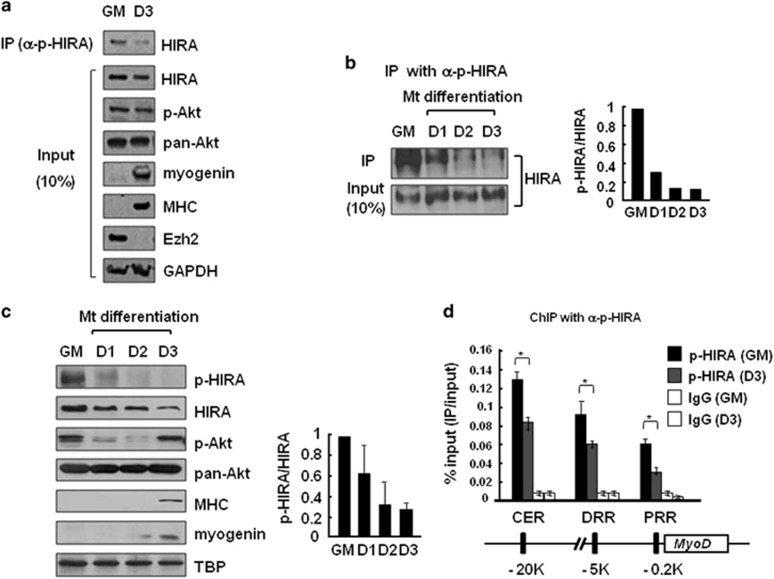
Figure 3.
HIRA phosphorylation decreases during muscle cell differentiation. The levels of the indicated proteins were monitored in C2C12 cells grown in growth (GM) or differentiating medium for 3 days (D1–3). (a, b) C2C12 cell extracts prepared from myoblasts and myotubes were subjected to IP using an anti-p-HIRA antibody and immunoblotted with an anti-HIRA antibody. Myogenin, MHC and Ezh2 were used as differentiation markers. The p-HIRA/HIRA protein signal ratio in each sample was quantitated and compared through normalization. (c) Whole-cell extracts were analyzed by western blotting using the indicated antibodies. TBP (TATA-binding protein) served as the loading control. The p-HIRA/HIRA protein signal ratio was obtained as above from two independent experiments. (d) ChIP using an anti-p-HIRA antibody was performed to monitor the recruitment of p-HIRA on MyoD regulatory regions in C2C12 myoblasts (GM) and myotubes (D3). Chromatin solutions prepared from each were subjected to IP using an anti-p-HIRA antibody and analyzed in duplicate via quantitative real-time-PCR to measure the relative enrichment of p-HIRA at the indicated loci. The data represent the percentages of ChIP (IP/Input). Error bars represent s.d., n=2. *P<0.05. CER, core enhancer region; ChIP, chromate immunoprecipitation; DRR, distal regulatory region; PRR, proximal regulatory region; siRNA, small interfering RNA.