Fig. 5.
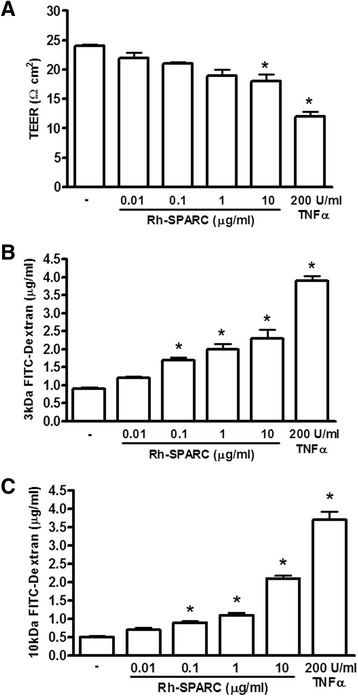
SPARC influences hCMEC/D3 barrier function measured by TEER and permeability. a Confluent hCMEC/D3 on transwell inserts were replenished with media containing rh-SPARC (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10 μg/ml) for 24 h then tested for TEER and transendothelial diffusion of FITC-labeled dextran (3 and 10 kDa). Compared to the untreated conditions, TEER measurements reflect a dose-dependent reduction in electrical impedance with increasing rh-SPARC concentration reaching significance with 1 μg/ml or greater rh-SPARC. Permeability assays using b 3 and c 10 kDa FITC-dextran revealed exposure of hCMEC/D3 to 0.1–10 μg/ml rh-SPARC enhanced permeability to both by 24 h of exposure. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test vs. untreated controls, *P < 0.05
