FIG 4.
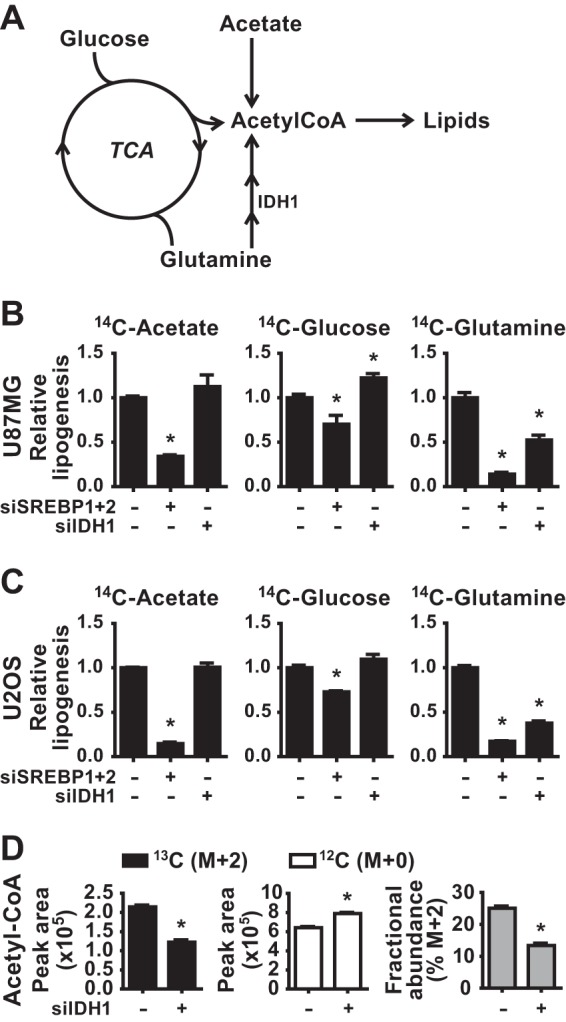
Effects of SREBP and IDH1 on de novo lipid synthesis from different carbon sources. (A) Diagram of the distinct paths of carbon from acetate, glucose, and glutamine to the acetyl-CoA required for lipid synthesis. (B and C) Incorporation of [1-14C]acetate, [U-14C]glucose, or [U-14C]glutamine into the lipid fraction was measured in U87MG (B) and U2OS (C) 72 h posttransfection with siRNAs targeting SREBP1 and -2 or IDH1. (D) Normalized peak areas of 13C-labeled (M+2) and unlabeled (M+0) acetyl-CoA and the fractional abundance of 13C-labeled acetyl-CoA M+2 measured by LC-MS/MS in metabolite extracts from U2OS cells 72 h posttransfection with nontargeting control siRNAs (−) or siRNAs targeting IDH1. Cells were labeled with [U-13C]glutamine for 2 h. Data are representative of two independent experiments. In panels B to D, the data are presented as means ± the SEM (n = 2; *, P < 0.05 relative to cells transfected with control siRNAs).
