Fig. 4.
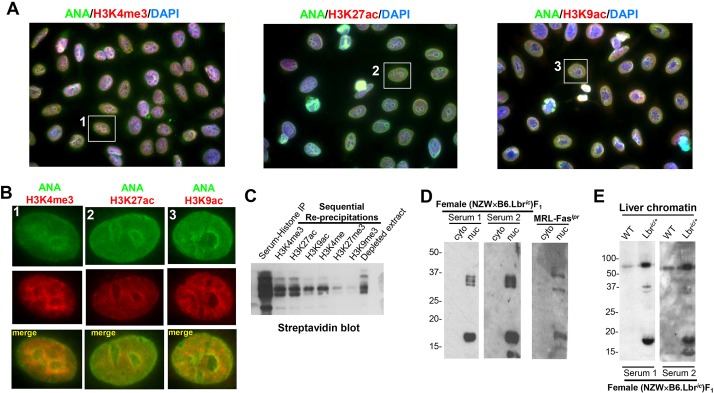
Female (NZW×B6.Lbric)F1 mice develop anti-nuclear autoantibodies recognizing histone H3 modifications associated with gene activation. (A) Co-localization of anti-nuclear reactivity and the activation-associated histone H3 modifications H3K4me3 (left panel), H3K27ac (middle panel), and H3K9ac (right panel). Anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) staining in the female (NZW×B6.Lbric)F1 serum was detected with an Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody, anti-modified H3 histones were detected by an Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Image magnification, 1000×. The individual red, green and blue color channels demonstrating the co-localization of the homogenous component of anti-nuclear autoantibody reactivity with modified histones are presented in Fig. S4. (B) Digital enlargement of the individual cells indicated in A. Anti-nuclear staining mediated by the (NZW×B6.Lbric)F1 serum is shown in the green channel, and the indicated modified histone is counterstained in the red channel. The yellow overlap signal represents nuclear co-localization of mouse serum immunoreactivity with anti-modified H3 histones. (C) Histones purified from HeLa cells were biotinylated in vitro, immunoprecipitated with (NZW×B6.Lbric)F1 mouse sera, collected on Protein A/G sepharose beads, washed, and eluted. The contents of the recovered histone extracts, consisting of histones that were specifically recognized by (NZW×B6.Lbric)F1 mouse sera, were sequentially re-precipitated with rabbit sera recognizing H3K4me3, H3K27ac, H3K9ac, H3K4me, H3K27me3, H3K9me3. Samples prepared from histone extracts collected from each step before, during, and after the re-precipitation process were blotted using peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin and enhanced chemiluminescence. (D) Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts prepared from 1×106 B6 mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were resolved using a 12% SDS-PAGE gel, and immunoblotted with sera from two female (NZW×B6.Lbric)F1 mice, and pooled sera from aged female MRL-Faslpr mice. Serum staining from a representative female (NZW×B6)F1 mouse, and verification of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractionation, is presented in Fig. S5. (E) Chromatin (5 µg) was isolated from the liver of female wild-type B6 and B6.Lbric/+ mice, and immunoblotted with serum from two female (NZW×B6.Lbric)F1 mice.