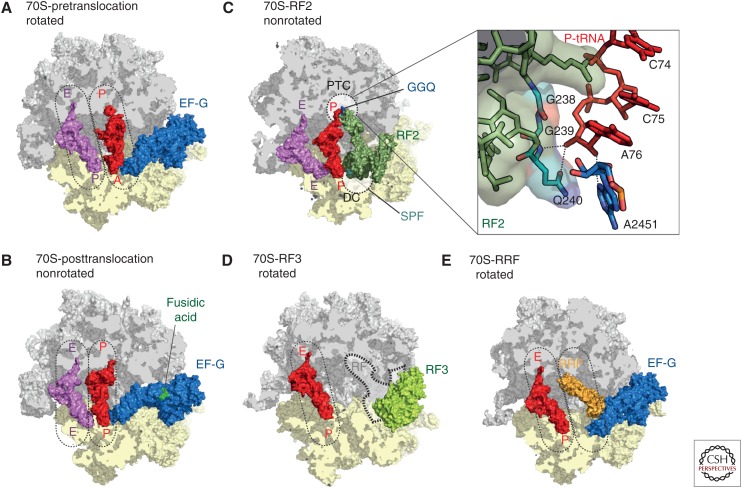
Figure 5.
The prokaryotic ribosome. Crystal structures of the ribosome bound with elongation factor G (EF-G) in the (A) pre- (Brilot et al. 2013), and (B) posttranslocation state (Lin et al. 2015), with 30S subunit (yellow), 50S subunit (gray), EF-G (blue), P-transfer RNA (tRNA) (red), E-tRNA (pink), and fusidic acid (green). (C) Crystal structure of RF2 (dark green) bound to the poststate ribosome with P-tRNA (red) and E-tRNA (pink) (Weixlbaumer et al. 2008). The peptidyltransferase center (PTC) on the 50S (gray) and the DC on the 30S subunit (yellow) are indicated as dashed lines. The insert zooms onto the PTC showing the GGQ motif of RF2 interacting with the CCA-end of the P-tRNA. (D) Crystal structure of RF3 (pale green) bound to the rotated 70S ribosome (Zhou et al. 2012b) with superimposed position of the P/E hybrid tRNA (red) (Brilot et al. 2013). The position of class I release factors is indicated with dashed lines. (E) Crystal structure of ribosome recycling factor (RRF, orange) bound to the rotated ribosome (Borovinskaya et al. 2007a) with superimposed positions of P/E hybrid tRNA (red) and prestate EF-G (blue) (Brilot et al. 2013).