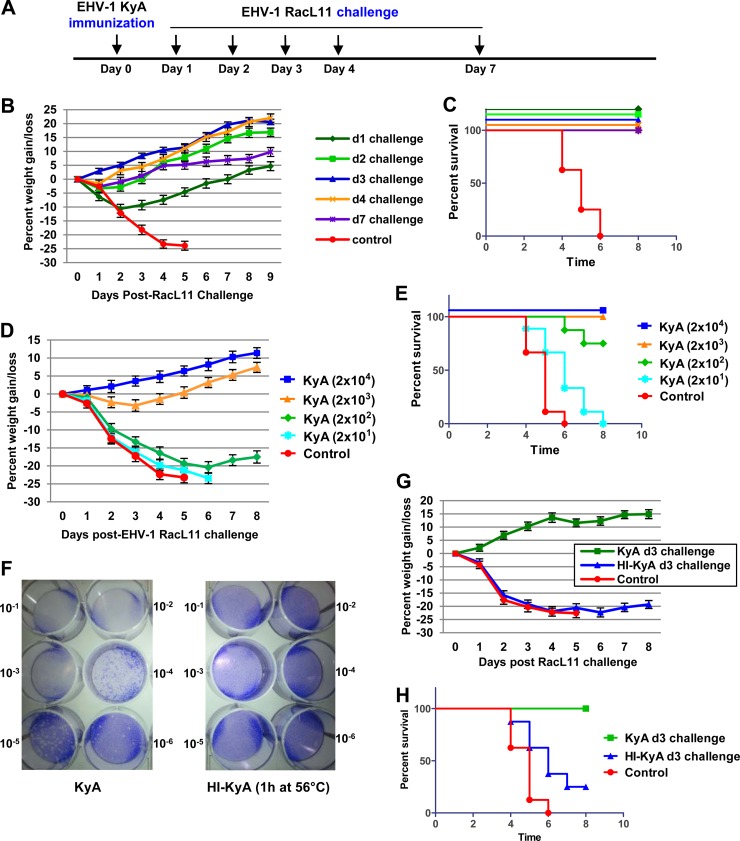
FIG 2.
Live EHV-1 KyA, but not heat-inactivated KyA, protected CBA mice from challenge with pathogenic EHV-1 RacL11 at 1 to 7 days postimmunization. (A) Schematic representation of immunization and EHV-1 challenge infection of CBA mice. (B and C) Average body weights (B) and percentages of survival (C) of CBA mice challenged with RacL11 at 1 to 7 days postimmunization. (D and E) Low-dose KyA immunization protects CBA mice from challenge with 1.5 × 106 PFU/mouse of RacL11. Average body weights (D) and percentages of survival (E) are shown. CBA mice (n = 8) were immunized with 2 × 101, 2 × 102, 2 × 103, or 2 × 104 PFU/mouse of KyA and were challenged with RacL11 (1.5 × 106 PFU/mouse) at 3 days postimmunization. (F to H) Heat-inactivated KyA (HI-KyA) could not protect CBA mice from RacL11 challenge. (F) EHV-1 KyA was inactivated by incubation at 56°C for 1 h (14). The amount of infectious EHV-1 was determined in equine NBL6 cells by standard plaque titration (50). Crystal violet stains the cells, allowing visualization of the clear plaques. The viral concentrations in the stained plates decrease from the top left (10−1) to the bottom right (10−6). (G and H) Average body weights (G) and percentages of survival (H) of CBA mice challenged with RacL11 at 3 days postimmunization. CBA mice (n = 8) were first immunized with medium (control), KyA (2 × 106 PFU/mouse), or HI-KyA (equivalent to 2 × 106 PFU prior to inactivation/mouse) and then challenged with RacL11 (1.5 × 106 PFU/mouse) at 3 and 14 days postimmunization.