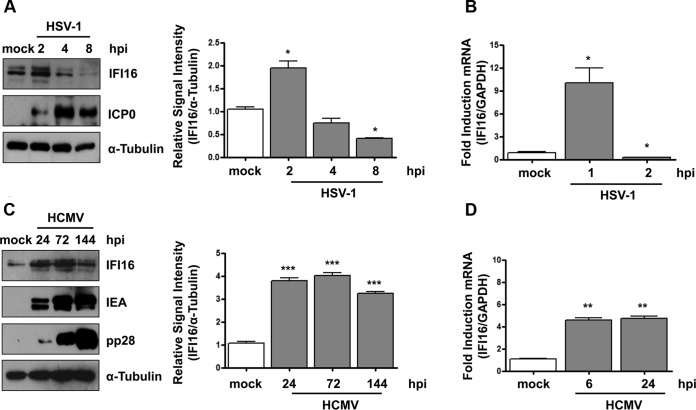
FIG 5.
IFI16 protein is stably expressed during HCMV infection. (A) HFF cells were mock infected or infected with HSV-1 at an MOI of 1. (Left) Protein levels of IFI16 and ICP0 were assessed at different times postinfection (hpi) by Western blotting. (Right) IFI16 protein was subjected to densitometry and normalized to α-tubulin, serving as a loading control. The data show the mean values ± SD from three experiments (*, P < 0.05 by unpaired t test). (B) Kinetics analysis of IFI16 mRNA expression in HFFs upon HSV-1 infection at an MOI of 1 by RT-qPCR. IFI16 mRNA expression was normalized to that of GAPDH and is shown as the mean ± SD fold changes following HSV-1 versus mock infection (*, P < 0.05 by unpaired t test). (C) HFFs were mock infected or infected with HCMV v65Rev (MOI of 1). (Left) Lysates were prepared at the indicated time points and subjected to Western blot analysis for IFI16, IEA, and pp28. IFI16 protein was subjected to densitometry and normalized to α-tubulin, which served as a loading control. The data show the mean values ± SD from three experiments (***, P < 0.001 by unpaired t test). (D) Kinetics analysis of IFI16 mRNA expression in HFFs upon HCMV infection at an MOI of 1 by RT-qPCR. IFI16 mRNA expression was normalized to that of GAPDH and is shown as the mean ± SD fold change following HCMV versus mock infection (**, P < 0.05 by unpaired t test).