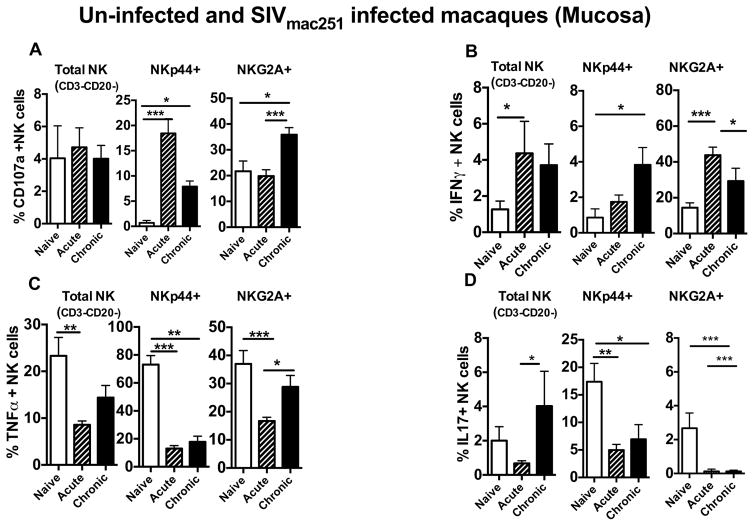
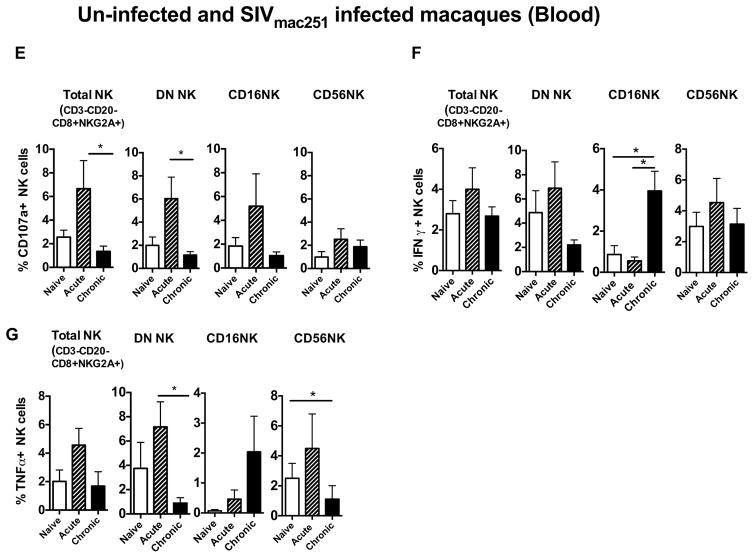
Figure 4. Alteration of functional capability during acute and chronic SIV infection in rectal mucosal NK cell subsets.
Bar graphs represent the average and standard deviation for (A) expression of CD107a (B) and levels of IFN-γ, (C) TNF-α and (D) IL17 secretion following a 12 hour stimulation with phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA)/ionomycin for the subsets of NK cells in rectal mucosa of naïve, SIV acute and SIV chronically infected rhesus macaques. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stimulated with 721.122 cells at E:T ratio of 5:1 for 12 hours and measured (E) CD107a, (F) IFN-γ and (G) TNF-α production on Total, CD16, CD56 and DN NK cells subsets in naïve, acute and chronically SIV infected animals. Data represents the seven animals per group. Kruskal-Wallis tests were used for comparisons of each group. Only significant P values are shown (*P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001).