Figure 6. APIP interacts with ERBB3 via its C-terminus.
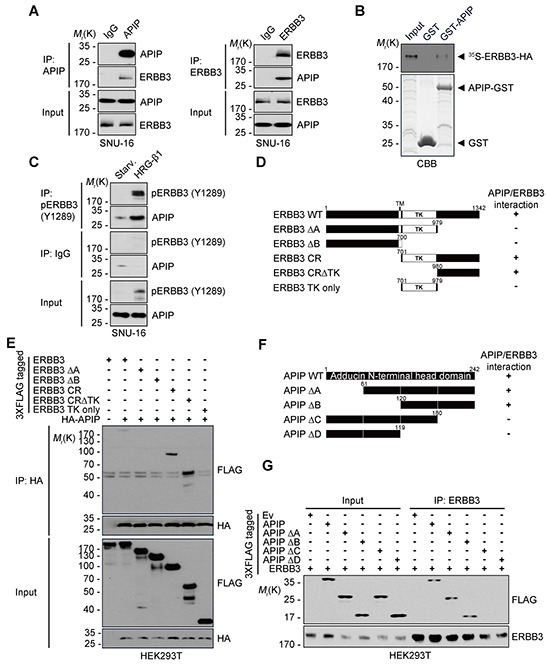
A. Co-immunoprecipitation of APIP and ERBB3 in SNU-16 cells. Whole cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) assay with anti-APIP (left) or anti-ERBB3 (right) antibody. B. In vitro binding assay. In vitro translated and 35S-methionine-labeled ERBB3 protein was incubated with the purified GST or GST-APIP protein immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose 4B beads. The bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography (upper) and CBB staining (lower). C. APIP binds to ERBB3 in a HRG-β1-dependent manner. SNU-16 cells were treated with 50 ng/ml HRG-β1 for 10 min and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) assay. D. Schematic representation of ERBB3 and its deletion mutants (Δ). The binding activities of ERBB3 WT and mutants to APIP are summarized based on the results in (E). E. Mapping of APIP-binding domain within ERBB3. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with pHA-APIP and either pERBB3-3xFLAG or deletion mutant for 24 h and whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) assay. F. Schematic representation of the conserved domains of APIP and its deletion mutants (Δ). The binding activities of APIP WT and mutants to ERBB3 are summarized based on the results in (G). G. The C-terminal region of APIP is essential for the binding to ERBB3. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed as in (E).
