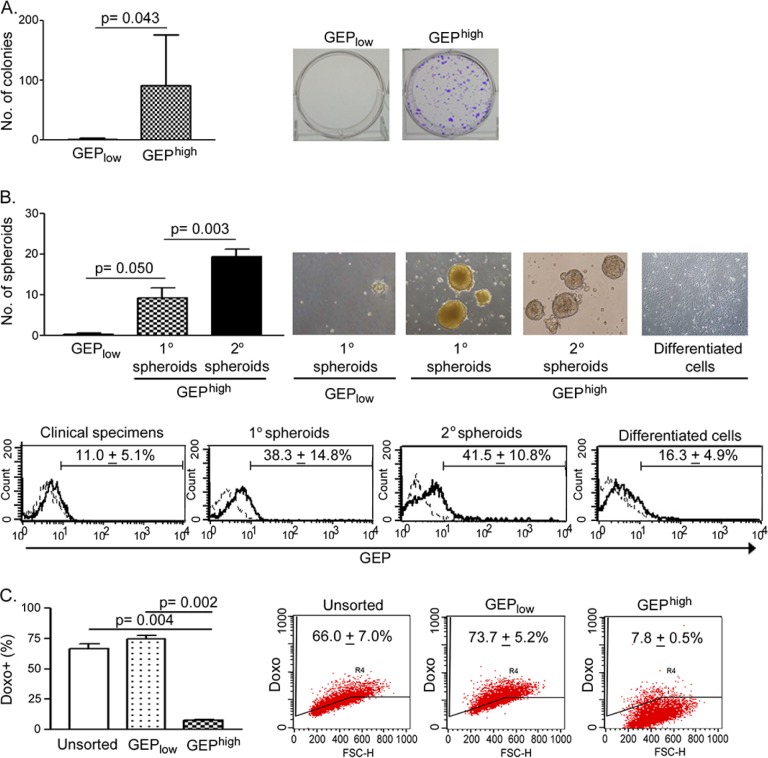
Figure 2. GEPhigh cells possess CSC properties in vitro.
A. Sorted GEPhigh cells isolated from freshly resected HCC were able to form more colonies than GEPlow cells (n = 6). In brief, 1000 cells of each freshly sorted subpopulation were seeded onto 6-well plate and allowed to grow for a month. B. Upper panel: GEPhigh cells, but not GEPlow cells, isolated from freshly resected tumors were able to generate primary (1°) spheroids (n = 3). 1° spheroids were collected and dissociated, and 1000 disaggregated cells were allowed to grow for 1 month for generating secondary (2°) spheroids (n = 3). GEPhigh cell-derived, but not GEPlow cells-derived 1° spheroids, were able to generate 2° spheroids. Following induced differentiation, disaggregated cells generated from GEPhigh cell-derived 2° spheroids differentiated and grew as adherent cells. Lower panel: Flow cytometric analysis showed the enrichment of GEP expression in mechanically dissociated GEPhigh cells-derived spheroids as compared to the original resected tumors (clinical specimens) and the differentiated adherent counterpart. Briefly, 1000 cells of each freshly sorted subpopulation were seeded into ultra-low attachment 24-well plate, and allowed to grow for 1 month to generate spheroids. C. After exposure to doxorubicin (0.5μg/ml) for 24h, GEPhigh cells retained significantly less doxorubicin than GEPlow cells and unsorted control (n = 3). Data are expressed as mean percentage + SD.