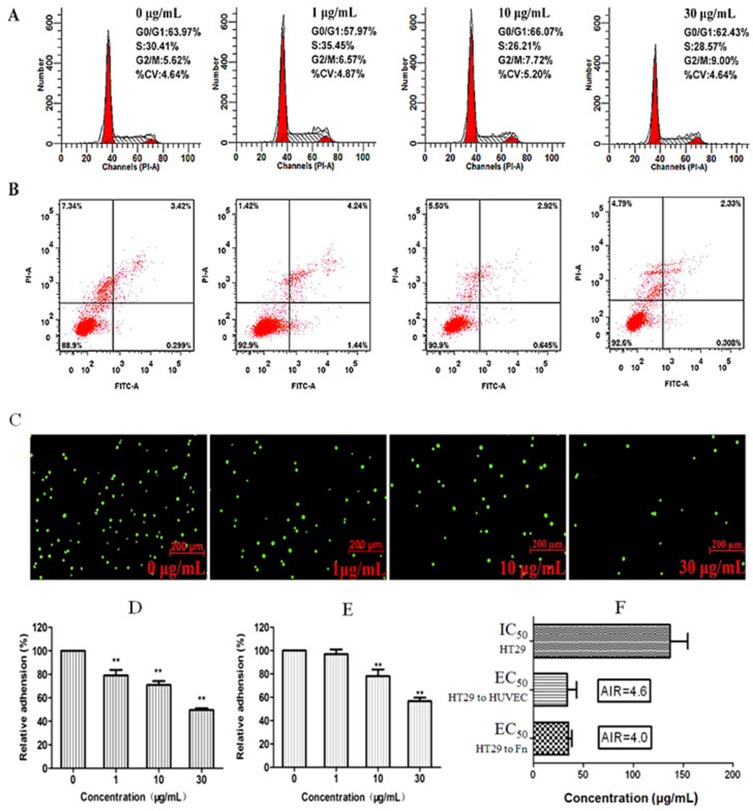
Figure 4. Low cytotoxicity of fraction G and its concentration-dependent (0, 1, 10, 30 μg/mL) inhibition on adhesion of cancer cell HT29 to human HUVECs and Fn-coated matrix.
There was no significant effect of G on HT29 cell cycle distribution (A) and apoptosis (B). However, G produced dose-dependent inhibition on Rhodamine 123-labeled HT29 cells adhered to the HUVEC monolayer stimulated by IL-1β (1 ng/mL) (C). (D) Quantitative inhibition of G on adhesion between HT29 cells and HUVEC monolayer. (E) Quantitative inhibition of G on adhesion of HT29 cells to Fn-coated matrix. (F) AIR indicated that G specifically inhibited hetero-adhesion between HT29 cells and HUVECs or Fn-coated matrix; the larger the AIR is, the more likely the drug works as an adhesion inhibitor. **P < 0.01, compared to the control.