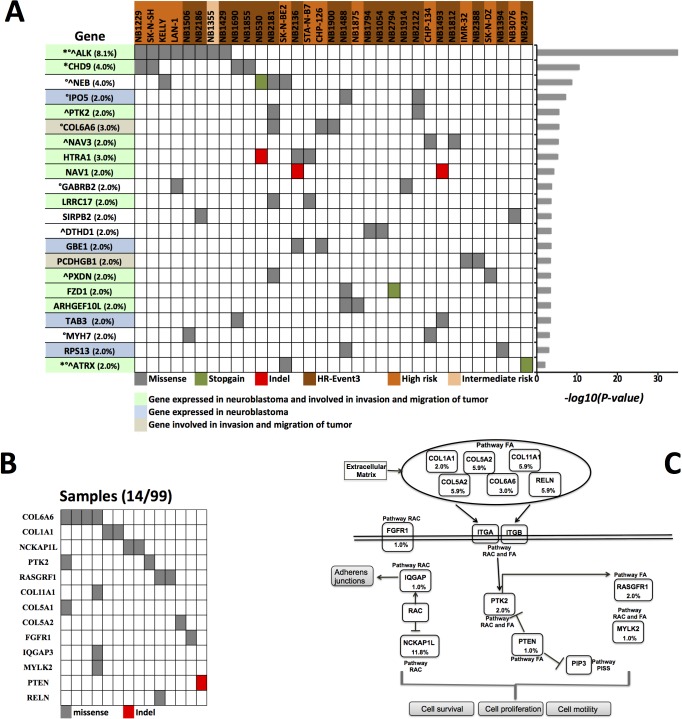
Figure 2. Prioritized genes and altered pathways.
A. Data matrix showing significantly mutated genes (FDR < 0.25 calculated with CHASM and FDR < 0.1 calculated with VEST) discovered in cases with clinically aggressive neuroblastoma by WES and DT-seq. The significance levels of the gene are plotted on the right. *Cancer Gene Census. Mouse insertional mutagenesis experiments support CHD9 as cancer causing gene. °Gene found mutated with non-silent mutations in previous studies on primary neuroblastoma [8-11]. ^Gene found mutated with non-silent mutations in previous studies on relapsed neuroblastoma [12, 13]. In parenthesis the frequency of cancer driver mutations calculated on 99 samples. B. Somatic mutations of the focal adhesion (FA) and regulation of actin cytoskeleton (RAC) pathways. Shown is the mutation status of the genes of the FA and RAC pathway in the 14 neuroblastomas (12 HR-Event3 and 2 high-risk) that carry at least 1 non-silent mutation. C. The key genes of the FA and RAC pathways with mutation frequencies in neuroblastoma are shown (Fig. adapted from KEGG pathway database). The frequency for COL11A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, IQGAP3, RELN, NCKAP1L were estimated from 17 samples analyzed by WES. The frequencies for COL6A6, COL1A1, FGFR1, PTEN, PTK2, RASGRF1, MYLK2 are from 99 samples analyzed by WES and DT-seq. PISS: Phosphatidylinositol signaling system.