Figure 5. miR-448-mediated inhibition of KDM2B induces Myc expression and glycolysis.
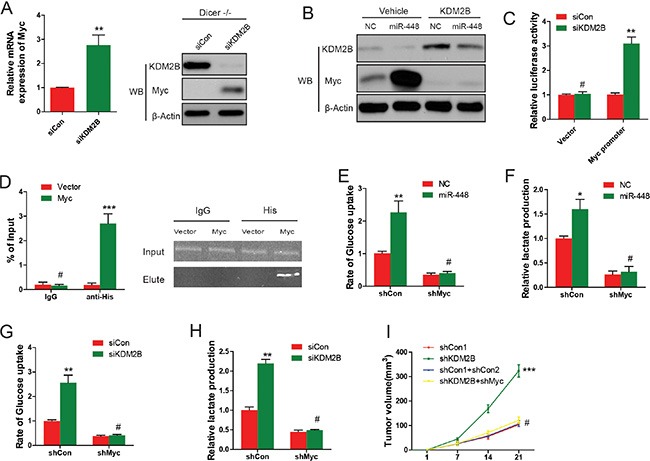
(A) Myc expression in GC cells or Dicer−/− MEF cells infected with KDM2B siRNAs was analyzed using qRT–PCR and Western blotting. (B) Myc protein expression in GC cells stably expressing KDM2B and further infected with miR-448 was analyzed using Western blotting. (C) The activity assay of Myc promoter upon KDM2B depletion by siRNAs in GC cells. Empty pGL3-enhancer plasmid was used as a control. (D) ChIP–qPCR analysis of Myc promoter. (E) and (F) Glucose uptake and lactate production were measured in GC cells expressing Myc shRNA and further infected with miR-448. (G) and (H) Glucose uptake and lactate production were measured in GC cells stably expressing Myc shRNA and further infected with KDM2B siRNA. (I) shMyc significantly reverted the positive effect shKDM2B on GC growth.
