Figure 5. MG53 can cross the blood-brain-barrier to target to injured brain tissue.
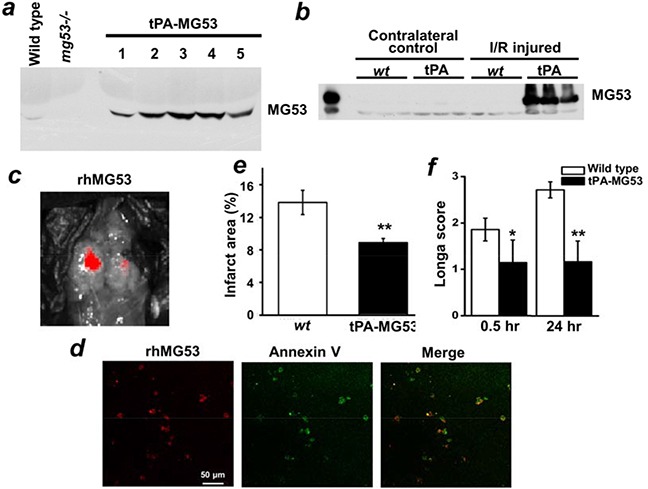
a. Serum samples from wt, mg53−/− and tPA-MG53 mice were subjected to immunoblotting against MG53. The results showed tPA-MG53 expressed high level of MG53 in blood circulation. Western blotting b. showed that circulating MG53 targets to injury side of brain upon ischemic surgery. c. IVIS spectrum in vivo imaging showed rhodamine-labelled rhMG53 can target to the injured brain area, which was further confirmed by co-staining of rhodamine-labelled rhMG53 (red) and Annexin V-FITC (green) in brain slices d. When tPA-MG53 mice were subjected to I/R injury to the brains, they displayed resistance to I/R injury as compared to wt control, as evidenced by reduced infarct area e. and decreased Longa score f.
