Figure 4. Identification of protease-mediated cleavage sites in APE1 and inhibition of this proteolysis by acetylation.
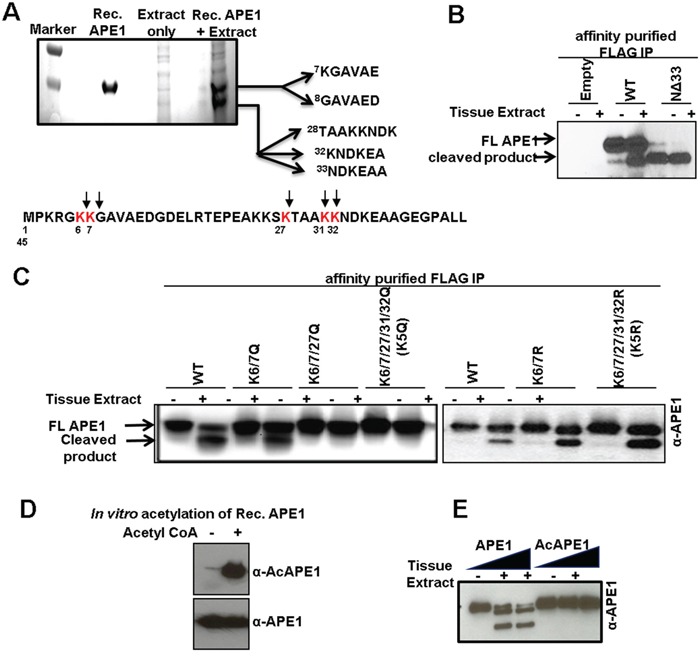
A. Coomassie Blue-stained SDS-PAGE for N-terminal sequencing shows two cleaved APE1 isoforms; the N-terminal 1-45 aa sequence of APE1 showing cleavage sites (bottom panel). B. Western blot analysis of FLAG-immuno-affinity purified FLAG-tagged WT APE1, N-terminal 33 aa deleted (NΔ33) mutant incubated ± tissue extract in the absence of PI. C. Western blot analysis of FLAG-immuno-affinity purified FLAG-tagged WT APE1, or site specific mutants incubated ± tissue extract in the absence of PI. D & E. Rec. APE1 was in vitro acetylated followed by Western blot analysis with α-AcAPE1, α-APE1 Abs (D) to confirm acetylation, and (E) incubated with normal tissue extract followed by Western blot analysis.
