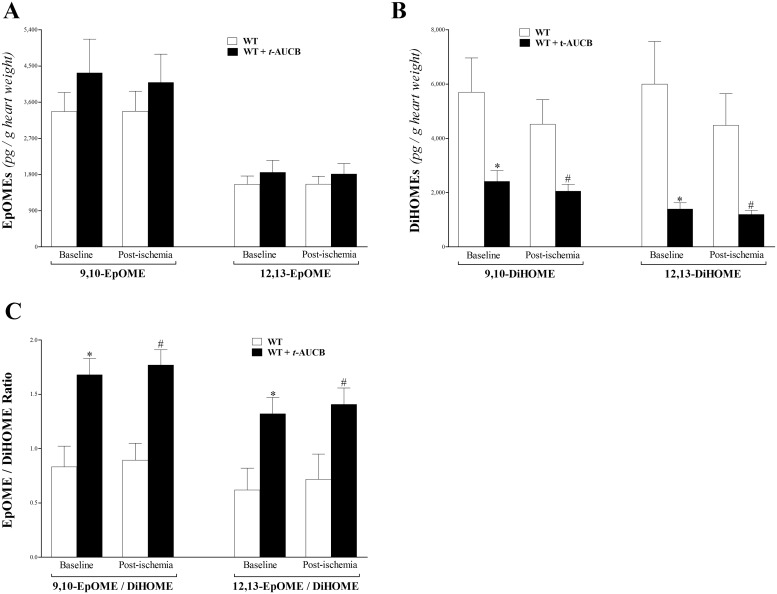
Fig 5. LC–MS/MS analysis of EpOME and DiHOME levels and the EpOME/DiHOME ratio in WT and t-AUCB-treated-WT mouse heart perfusates at baseline (pre-ischemia) and post-ischemia.
(A) 9,10- and 12,13-EpOME levels had an increasing trend at baseline and post-ischemia in t-AUCB-treated-WT versus WT mice, but this was not significant (p > 0.05). Neither EpOME was significantly changed post-ischemia compared to baseline in both groups. (B) 9,10- and 12,13-DiHOME levels decreased at baseline and post-ischemia in t-AUCB-treated-WT versus WT mice (p < 0.001). (C) The EpOME/DiHOME ratio increased in t-AUCB-treated versus WT mice at baseline and post-ischemia (p < 0.0001). The measured EpOME and DiHOME levels and EpOME/DiHOME ratio did not change post ischemia versus baseline within the same group (p > 0.05, A-C). * p < 0.05 versus baseline WT. # p < 0.05 versus post-ischemia WT. n = 8.