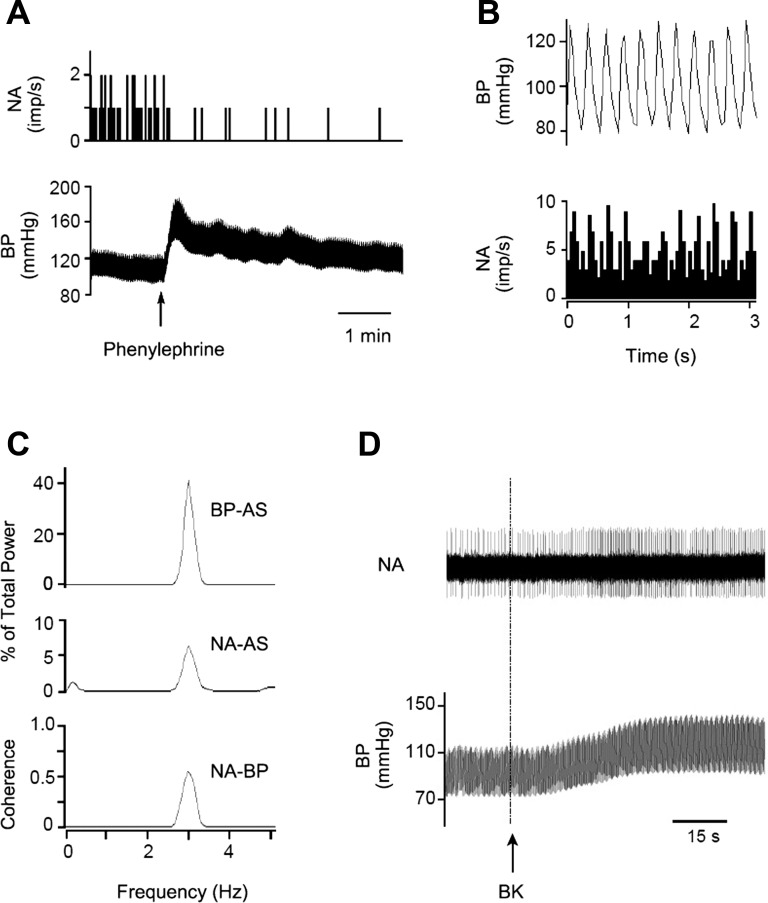
Fig. 3.
Identification of a cardiovascular neuron in the elPBN. A: phenylephrine increased blood pressure (BP) and reduced neuronal activity (NA). B: time domain analysis using pulse-triggered averaging shows a relationship between BP and NA. C: frequency domain analysis shows a significant coherence (0.65 with frequency of 2.89 Hz) between BP and NA. B and C demonstrate cardiac rhythmicity of the elPBN neuron. D: NA and BP in response to stimulation of cardiac sympathetic afferent nerves with epicardial application of bradykinin (BK). Top: neuronal traces displaying NA; bottom: original recordings of BP. Arrow indicates BK application. AS, autospectra.