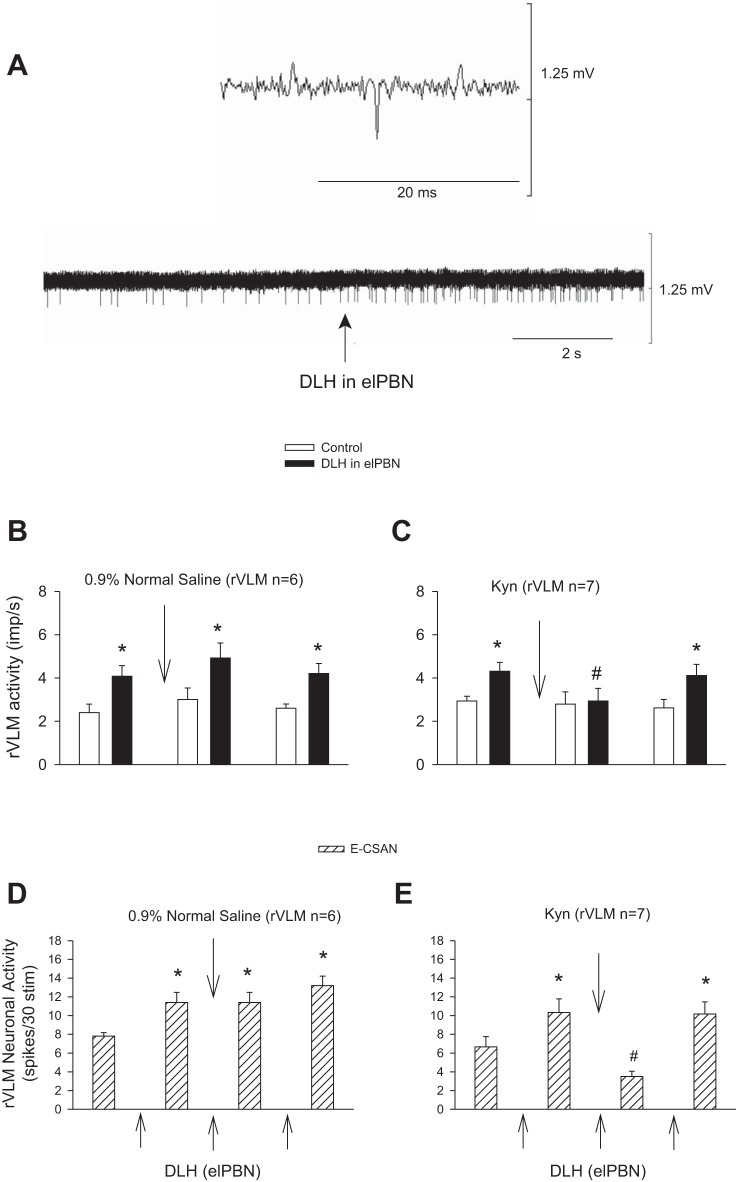
Fig. 9.
Activation of the elPBN through glutamate regulates rVLM activity in the absence and presence of CSAN stimulation. A: neuronal traces of an rVLM cardiovascular neuron in response to microinjection of dl-homocysteic acid (DLH, 2 nmol/50 nl) into the elPBN. An individual action potential is shown above traces. B and C: increased basal rVLM activity in response to microinjection of DLH into the elPBN. D and E: evoked rVLM activity induced by electrical CSAN stimulation (E-CSAN) in response to microinjection of DLH into the elPBN. DLH-enhanced basal and CSAN-evoked activity in the rVLM recovered 50–60 min after Kyn. *P < 0.05, after vs. before elPBN excitation with DLH. #P < 0.05, after vs. before iontophoresis of Kyn into the rVLM.