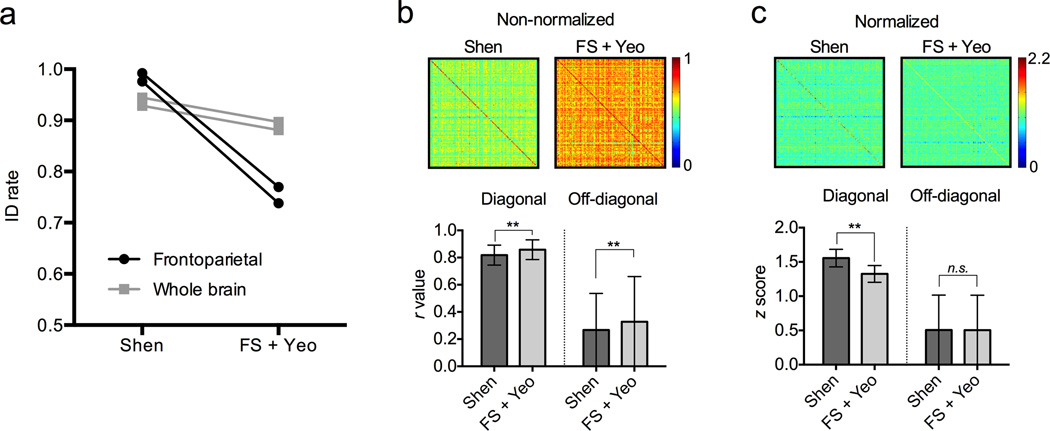
Figure 4. Effect of node and network scheme on identification accuracy.
a) Comparison of identification accuracy using the Shen node atlas and network definitions (left) versus the FreeSurfer (FS) node atlas and Yeo network definitions (right). Accuracy is numerically higher using the Shen scheme; the difference is exaggerated when using just the frontoparietal networks (black lines) relative to the whole brain (gray lines). b) Raw 126×126 cross-subject correlations of frontoparietal connectivity patterns from Rest 1 and Rest 2 (top; scale bar indicates r value). Row and column subject order is symmetric; thus, diagonal elements are correlation scores from matched subjects. Mean correlation coefficients for both diagonal (matched) and off-diagonal (unmatched) elements are shown in the bar graph at bottom (error bars represent ± s.d.). The overall correlation coefficients are higher using the FS+Yeo scheme, for both diagonal elements (n = 126) and off-diagonal elements (n = 15,876). **p < 10−5, two-tailed t-test. c) Cross-subject correlation matrices after z score normalization (top; scale bar indicates z score). The global difference in correlation values is eliminated since there is no significant difference in the off-diagonal z scores. However, correlations between diagonal elements are significantly higher using the Shen scheme than the FS+Yeo scheme (bottom; error bars represent ± s.d.), which helps account for the increase in identification accuracy using the Shen scheme. **p < 10−5, two-tailed t-test.