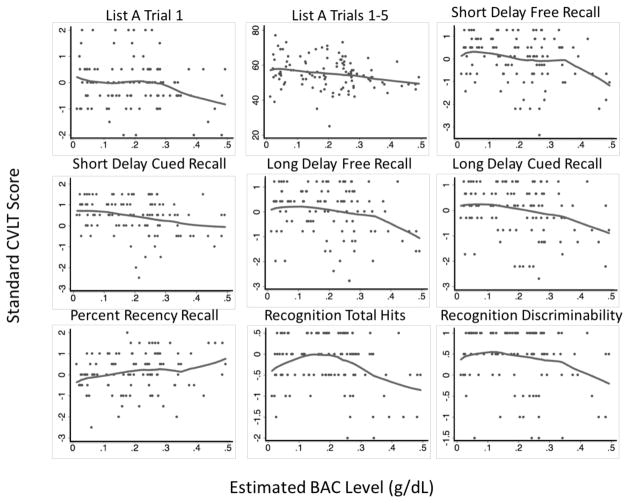
Figure 1.
Locally weighted scatterplot smoothing (LOWESS) regressions depict relationships between alcohol use and verbal learning and memory standard scores above and beyond baseline verbal learning and memory performance and attention problems and follow-up WRAT Reading performance. Based on the curvature and shape of LOWESS regressions, follow-up analyses utilized ordinary least squares regressions to examine the association between estimated peak blood alcohol level in the past 3-months and verbal learning and memory performance. All nine indices of verbal learning and memory showed significant linear relationships; there was also a significant quadratic relationship between recognition total hits and blood alcohol level (ps < .05).