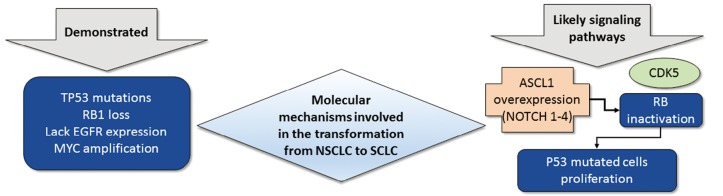
Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms involved in the transformation from NSCLC to SCLC. They include TP53 mutations, RB1 loss, lack of EGFR expression and MYC amplification. The most studied signaling pathway is the ASCL1 which is regulated by four different NOTCH receptors. NOTCH alterations promote ASCL1 and CD56 overexpression. These changes induce CDK5 activity and inactivation of RB by phosphorylation. With inactivated RB, p53 mutated cells have a selective advantage. NSCLC, non-small cell lung carcinoma; SCLC, small cell lung carcinoma; RB1, retinoblastoma 1; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; NOTCH, neurogenic locus notch homolog; ASCL1, achaete-scute homolog 1; CDK5, cyclin-dependent kinase 5.