Figure 3.
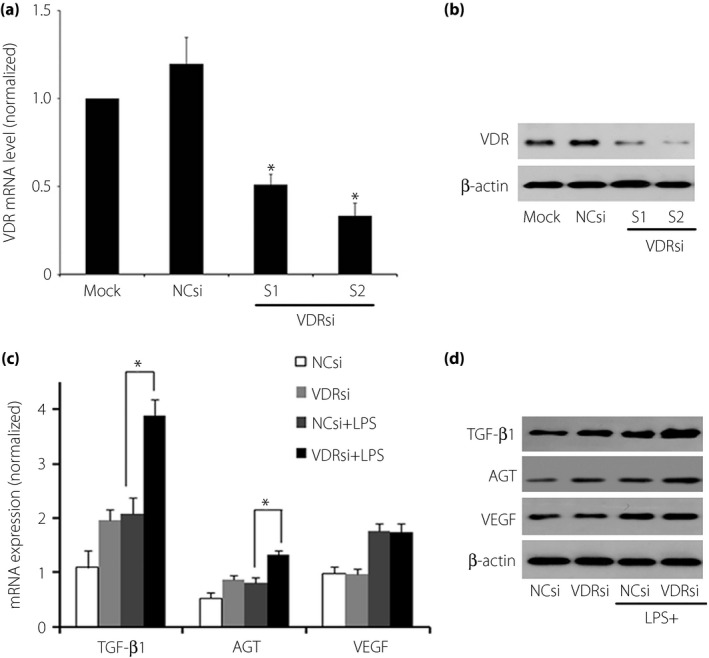
Effect of vitamin D receptor (VDR) small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) transfection on podocytes. After transfecting with VDR‐siRNA of target 1 or target 2 at the concentrations of 20 nmol/L transfection solution, decreases were observed both in (a) VDR messenger RNA (mRNA) and (b) protein expression compared with those of mock or negative siRNA transfection, respectively (P < 0.05). The target 2 siRNA was chosen as the experimental VDR‐siRNA because of a more thorough inhibition of VDR. After VDR‐siRNA transfection, transforming growth factor‐β (TGF‐β) and angiotensinogen (AGT) expression were further elevated at both (c) mRNA and (d) protein levels (P < 0.05), whereas the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression levels did not change significantly (P > 0.05). NCsi, negative control‐siRNA; VDRsi, VDR‐siRNA.
