Figure 5.
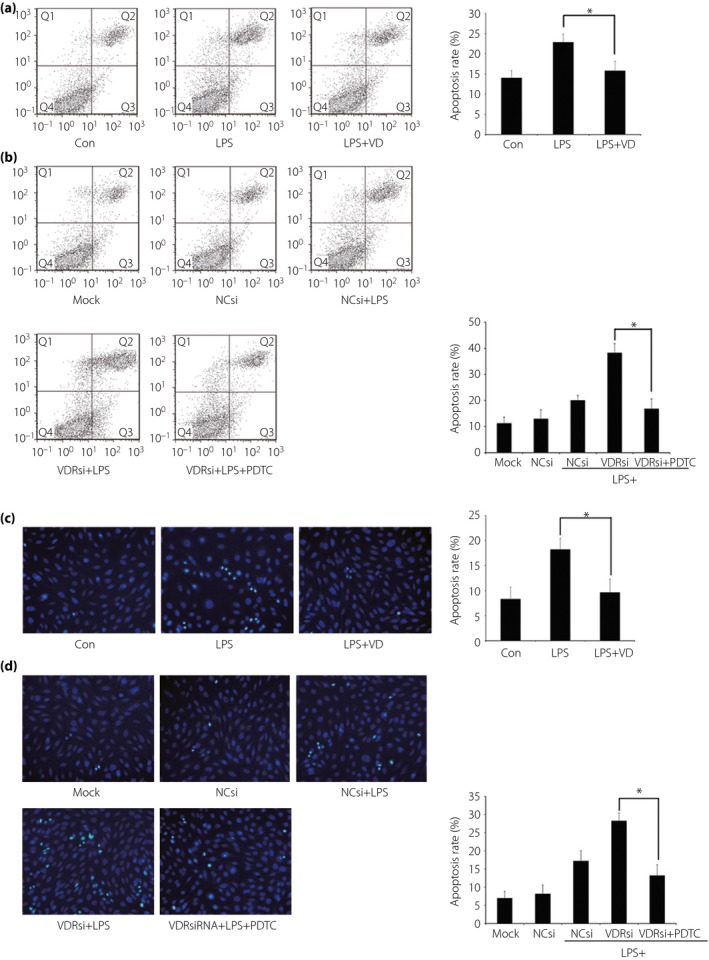
Effect of vitamin D (VD) and vitamin D receptor (VDR) small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) transfection on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‐mediated podocyte apoptosis. (a) Pre‐incubation with VD presented to protect podocytes from excessive apoptosis induced by LPS. (b) VDR‐siRNA transfection in podocytes resulted in further elevated apoptosis after LPS challenge. When the nuclear factor‐κB (NF‐κB) pathway was blocked by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), the apoptosis rate showed an extreme reduction. (a,b) The results detected through flow cytometry by using an Annexin V‐FITC/PI staining kit. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 in the figures represented dead cells, late apoptotic cells, early apoptotic cells and viable cells. Cell proportions of Q2 together with Q3 were calculated. (c,d) The results found through Hoechst 33 258 staining, which showed similar outcomes of (a) and (b), respectively. The apoptosis rate of cells was evaluated by scoring the cell numbers showing a pycnotic nucleus or fragmented nucleus. *P < 0.05. NCsi, negative control‐siRNA; VDRsi, VDR‐siRNA.
