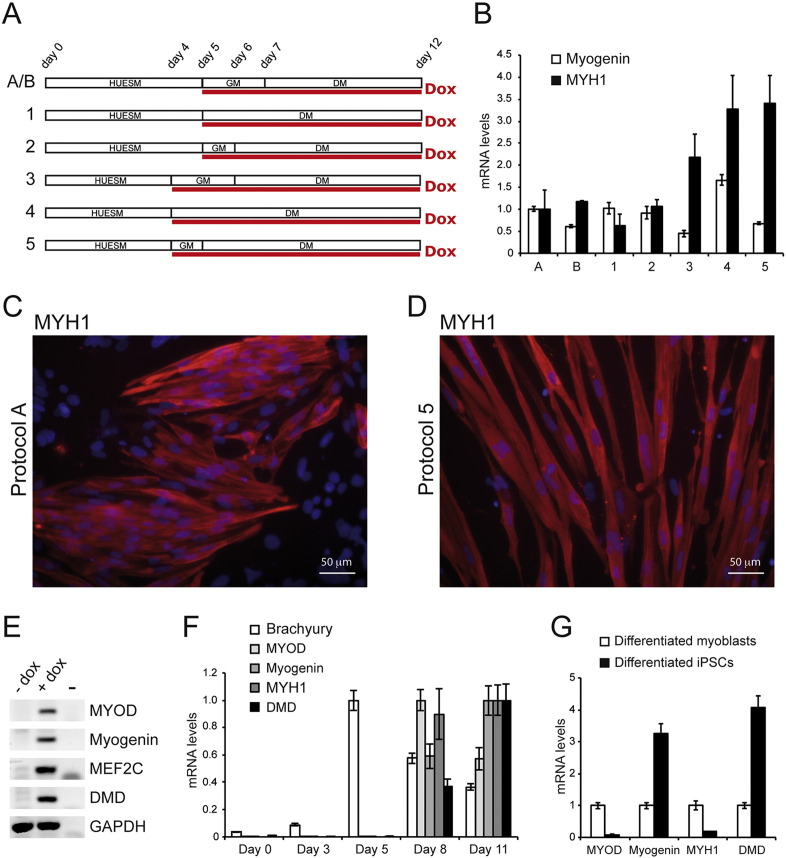
Fig. 2.
Optimization of the differentiation protocol.
(A) Diagrams of the variants of the differentiation protocol of WT I-MyoD cells. HUESM: iPSC differentiation medium; GM: myoblast growth medium; DM: myoblast differentiation medium. Red line: time in doxycycline (Dox). Time points of medium change are indicated above. See text for details. (B) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of Myogenin (white bars) or Myosin Heavy Chain (MYH1; black bars) in cells differentiated as depicted in panel (A). Relative levels of mRNA were calculated with the delta delta Ct method and condition A is used as the calibrator sample. Error bars: standard error from a triplicate. (C–D) Immunostaining for the muscle marker MYH1 in WT I-MyoD cells differentiated with protocol A (panel C) or 5 (panel D). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar for both panels: 50 μm. (E) RT-PCR analysis of muscle markers in WT I-MyoD cells differentiated with protocol 5 in absence (− Dox) or presence (+ Dox) of doxycycline. GAPDH is used as a housekeeping control. (F-G) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of the indicated markers in a time-course experiment using protocol 5 (panel F) and in differentiated iPSCs (protocol 5, day 11) compared with differentiated human myoblasts (panel G). Relative levels of mRNA were calculated with the delta delta Ct method. In panel F, for each marker the condition with higher expression has been used as the calibrator sample. In panel G, differentiated myoblasts represent the calibrator sample. Error bars: standard error from a triplicate.