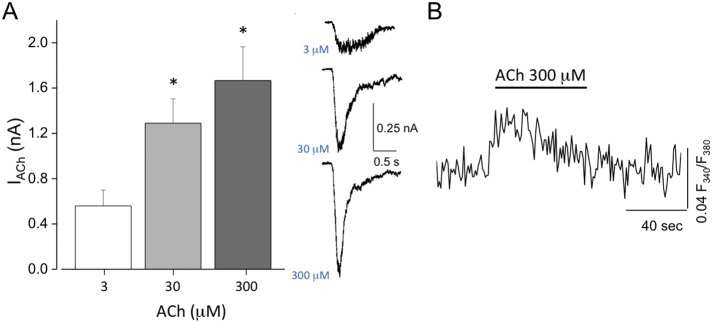
Fig. 3.
Functional properties of WT iPSC-derived skeletal muscle cells.
(A) Left panel: dose-response relation of ACh-evoked currents in skeletal muscle cells differentiated from WT I-MyoD iPSCs with the protocol 5 described in Fig. 2 (*, p < 0.05, OneWay ANOVA). Right panel: sample traces of the three concentrations of ACh applied to a WT iPSC-derived skeletal muscle cell. (B) Average fluorescence response to ACh (300 μM), in Fura-2-loaded skeletal muscle cell differentiated from WT iPSC with the protocol 5 described in Fig. 2 (n = 22).