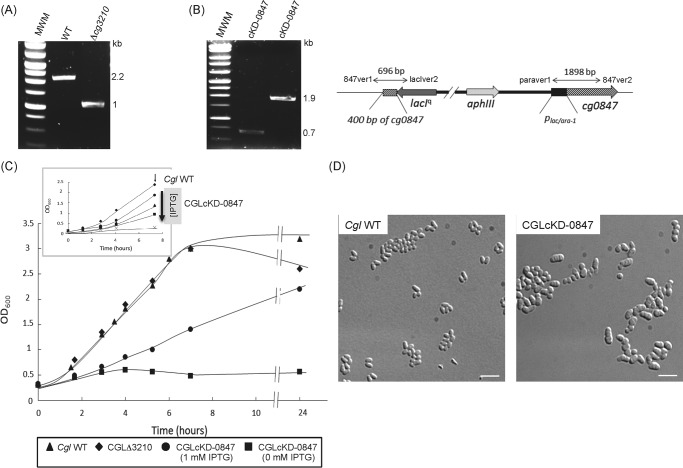
FIGURE 4.
Inactivation of cg0847 and cg3210 in C. glutamicum. A, evidence for allelic replacement at the cg3210 locus of C. glutamicum. The deletion of the entire cg3210 ORF results in the replacement of the WT 2,157-bp amplification signal by a 1,033-bp fragment in the knock-out mutant. B, schematic representation of the chromosomal region of the cg0847 knockdown mutant (CGLcKD-0847) after integration of the pZEΔ847 plasmid into cg0847. Evidence for the correct insertion of the plasmid by PCR analysis using the two sets of primers, 847ver1/lacIver2 (resulting amplicon: 696 bp) and paraver1/847ver2 (resulting amplicon: 1,898 bp). C, growth characteristics of C. glutamicum WT, CGLΔ3210, and CGLcKD-0847. The strains were grown in LB broth at 30 °C with shaking. Inset, growth of CGLcKD-0847 in the presence of 0 (crosses), 12.5 μm (squares), 25 μm (triangles), or 1 mm (circles) IPTG; C. glutamicum WT (diamonds). The arrow indicates the time point at which samples were removed for the cell wall analyses described in this study. D, optical micrographs of C. glutamicum WT and CGLcKD-0847 cells cultivated overnight in BHI medium. One droplet of culture was absorbed onto a microscope slide coated with 1% agarose and visualized using a DMIRE2 optical microscope (Leica) equipped with a CCD camera (CoolSNAP HQ2, Roper Scientific). Scale bar, 5 μm.