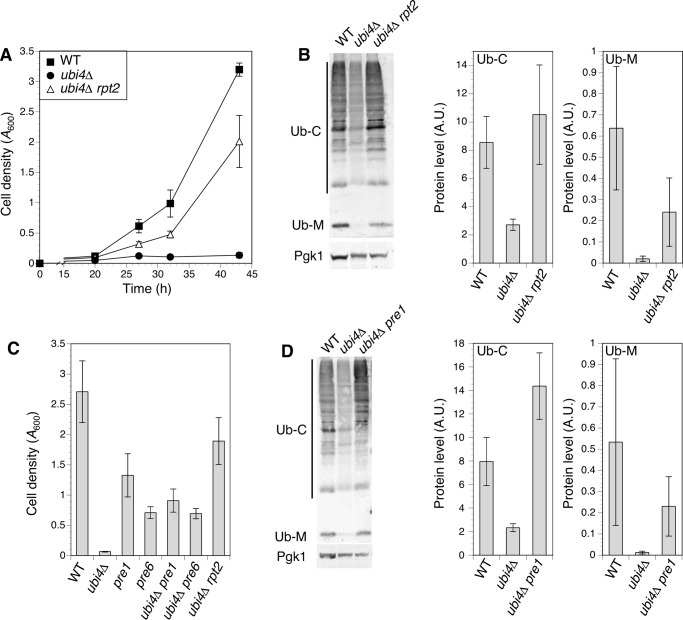
FIGURE 4.
Mutation of proteasome subunit genes restored ubiquitin supply and growth in zinc-deficient ubi4Δ cells. A, a recessive rpt2 allele suppressed the ubi4Δ growth defect in zinc-deficient conditions. Wild-type (BY4741), ubi4::KanMX4, and ubi4Δ rpt2E301K (CWM280) strains were grown to saturation in SD medium and inoculated into zinc-deficient (LZM + 1 μm ZnCl2) cultures. Growth was monitored by measuring cell densities. Each data point represents the mean of three independent cultures, and error bars show ±1 S.D. B, effect of the rpt2E301K suppressor mutation on ubiquitin accumulation. Strains listed in A were grown in zinc-deficient conditions and assayed for ubiquitin by immunoblotting. One representative immunoblot is shown. Pgk1 was detected as a loading control. Adjacent panels show quantitation of ubiquitin conjugates (Ub-C) and monomers (Ub-M) in three replicate immunoblots including the example shown. C, hypomorphic alleles of the PRE1 and PRE6 proteasomal subunit genes suppressed the ubi4Δ growth defect in zinc-deficient conditions. Cell densities of wild-type (BY4741), ubi4Δ (CWM260), pre1DAmP, pre6 DAmP, ubi4Δ rpt2E301K (CWM280), ubi4Δ pre1 DAmP (CWM278), and ubi4Δ pre6 DAmP (CWM279) strains were compared after 48 h of growth in zinc-deficient (LZM + 1 μm ZnCl2) medium as described for A. Means of three replicates are shown; error bars represent ± 1 S.D. D, wild-type (BY4741), ubi4Δ (CWM260), and ubi4Δ pre1DAmP (CWM278) cells were grown in zinc-deficient conditions and assayed for ubiquitin by immunoblotting. One representative immunoblot is shown, and Pgk1 was detected as a loading control. Adjacent panels show quantitation of ubiquitin conjugates (Ub-C) and monomers (Ub-M) in three replicate immunoblots including the example shown. A.U., arbitrary units.