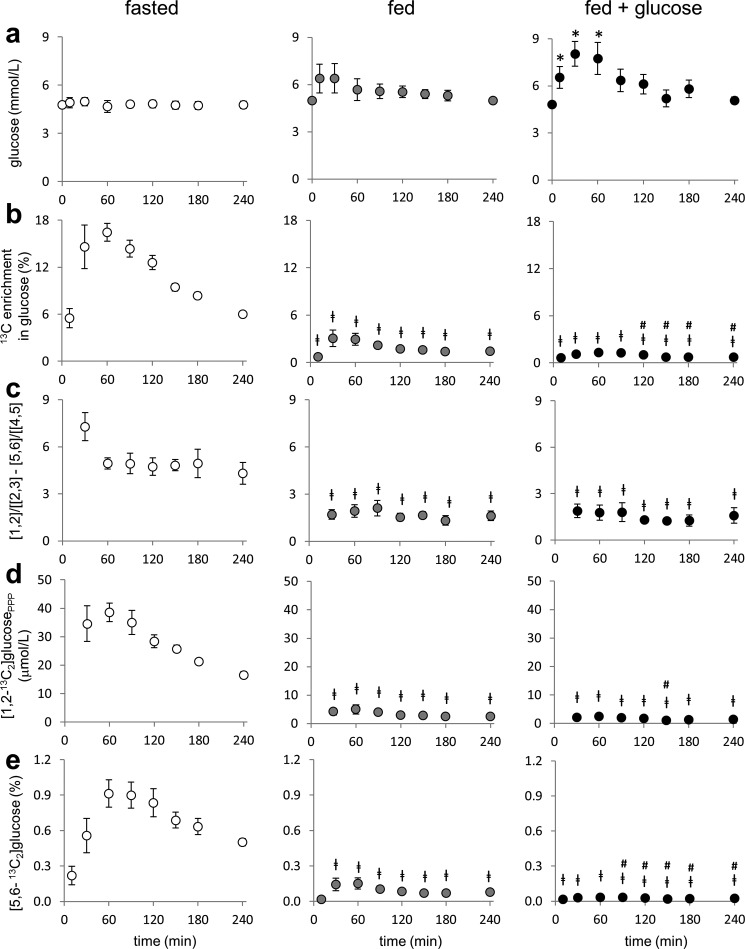
FIGURE 4.
Assessment of hepatic PPP and gluconeogenesis by analysis of plasma glucose from subjects receiving [U-13C3]glycerol. a, plasma glucose remained the same under a fast and a fed condition but increased under a fed plus glucose condition. b, 13C enrichment in glucose (reflecting gluconeogenesis from [U-13C3]glycerol) was higher under a fast condition than under a fed condition. The enrichment under a fed condition was slightly higher than a fed plus glucose condition at 120–240 min. The 13C enrichment in glucose represents the sum of all glucose isotopomers with excess 13C. c, as an index of hepatic PPP activity, the ratio difference between [1,2-13C2]/[2,3-13C2] and [5,6-13C2]/[4,5-13C2] in glucose was higher under a fast condition than under a fed condition, indicating that fasting induced the PPP activity. d, plasma [1,2-13C2]glucose produced through hepatic PPP was much higher under a fast condition than under a fed condition. e, the fraction of [5,6-13C2]glucose was greatest under a fast condition followed by a fed condition and a fed plus glucose condition. [5,6-13C2]Glucose was produced by [U-13C3]glycerol metabolism through the TCA cycle prior to gluconeogenesis. [1,2], [1,2-13C2]glucose; [2,3], [2,3-13C2]glucose, etc.; [1,2-13C2]glucosePPP, [1,2-13C2]glucose produced through the PPP. *, p < 0.05 compared with t = 0 within each graph; ‡, p < 0.05 compared with the corresponding time point under a fasted state; #, p < 0.05 compared with the corresponding time point under a fed state (n = 4–6).