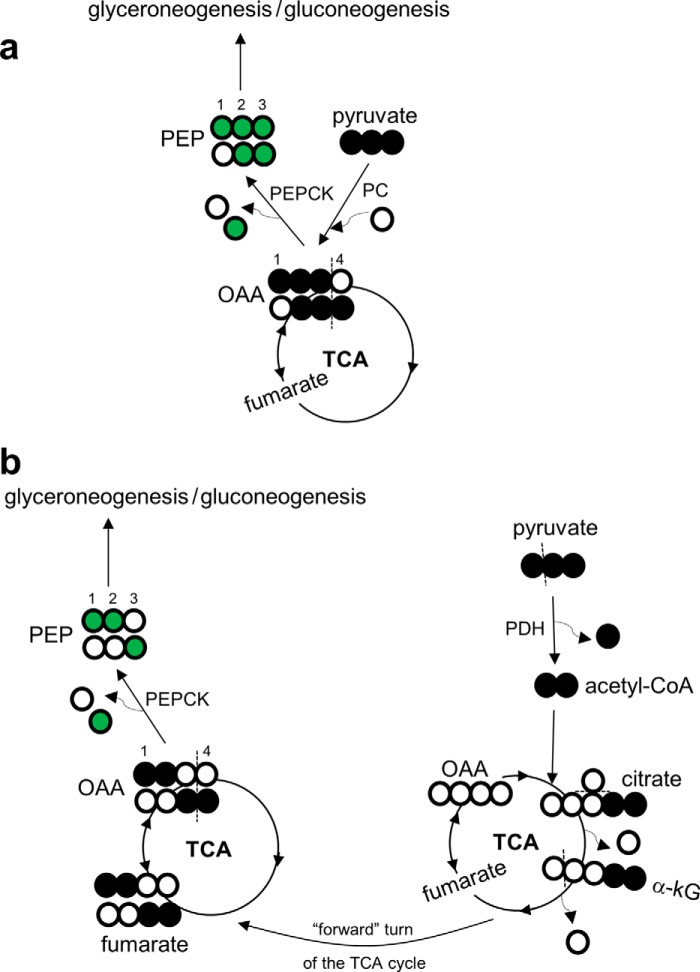
FIGURE 6.
Double-labeled trioses produced through the metabolism of [U-13C3]glycerol in the TCA cycle. After phosphorylation, [U-13C3]glycerol may be further metabolized to [U-13C3]pyruvate entering the TCA cycle. a, the entry of [U-13C3]pyruvate through pyruvate carboxylase produces [1,2,3-13C3]oxaloacetate, which equilibrates with the symmetric fumarate pool, producing both [1,2,3-13C3]- and [2,3,4-13C3]oxaloacetate. These oxaloacetate isotopomers may exit the TCA cycle through PEP carboxykinase generating [U-13C3]PEP and [2,3-13C2]PEP. b, the entry of [U-13C3]pyruvate through pyruvate dehydrogenase generates [U-13C2]acetyl-CoA. The condensation of [U-13C2]acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate produces [4,5-13C2]citrate and [4,5-13C2]α-ketoglutarate. After decarboxylation and experiencing a symmetric fumarate pool, [1,2,-13C2]- and [3,4-13C2]oxaloacetate are produced. These isotopomers become [1,2-13C2]PEP and [3-13C1]PEP through PEP carboxykinase. Open circle, 12C; black circle, 13C; green circle, 13C after metabolism through the TCA cycle. kG, ketoglutarate; OAA, oxaloacetate; PC, pyruvate carboxylase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase.