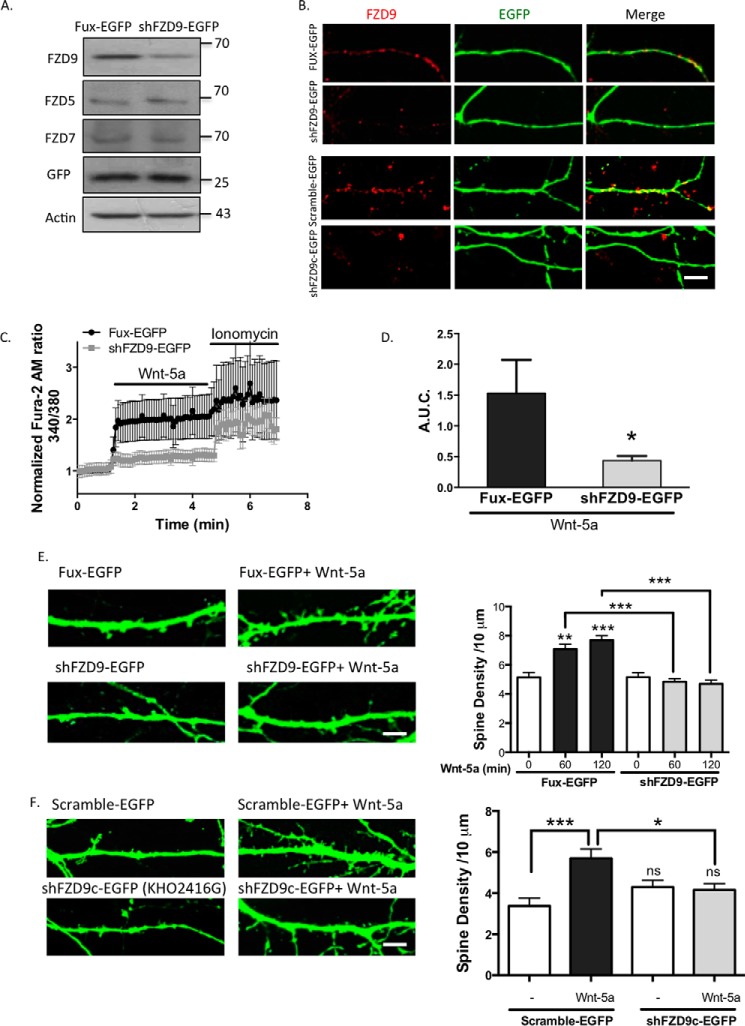
FIGURE 4.
FZD9 down-expression impairs Wnt-5a signaling. A, detection of FZD9, FZD5, and FZD7 protein levels in the homogenate of HT22 cells transfected with Fux-EGFP (control) or shFZD9-EGFP (the three FZD receptors were measured in three different membranes). Anti-GFP was used as a transfection control, and anti-actin was used as a loading control (n = 3). B, immunofluorescence of FZD9 (red) in FUX-EGFP/shFZD9-EGFP-transfected neurons (green) and in scramble-EGFP/shFZD9c-EGFP (commercial shFZD9, Cod. KH02416G) transfected neurons. Scale bar, 8 μm. C, measurement of the intracellular Ca2+ increase in hippocampal neurons transfected with Fux-EGFP (black plots) or shFZD9-EGFP (gray plots) after stimulation with Wnt-5a. Ionomycin was used as an ionophore to increase intracellular Ca2+ levels. D, quantification of A.U.C. (n = 4). E, left panel, representative images of the neurites from Fux-EGFP- or shFZD9-EGFP-transfected neurons treated with or without Wnt-5a for 2 h. Scale bar, 3 μm. Right panel, quantification of the spine density in control condition or after 1 or 2 h of Wnt-5a treatment (n = 3). F, left panel, representative images of Scramble-EGFP and shFZD9c-EGFP-transfected neurons (commercial shFZD9, Cod. KH02416G) treated or not with Wnt-5a for 2 h. Right panel, quantification of the density of dendritic protrusion per neurite length. Scale bar, 3 μm. ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. ns, no significant difference compared with the control.