FIGURE 3.
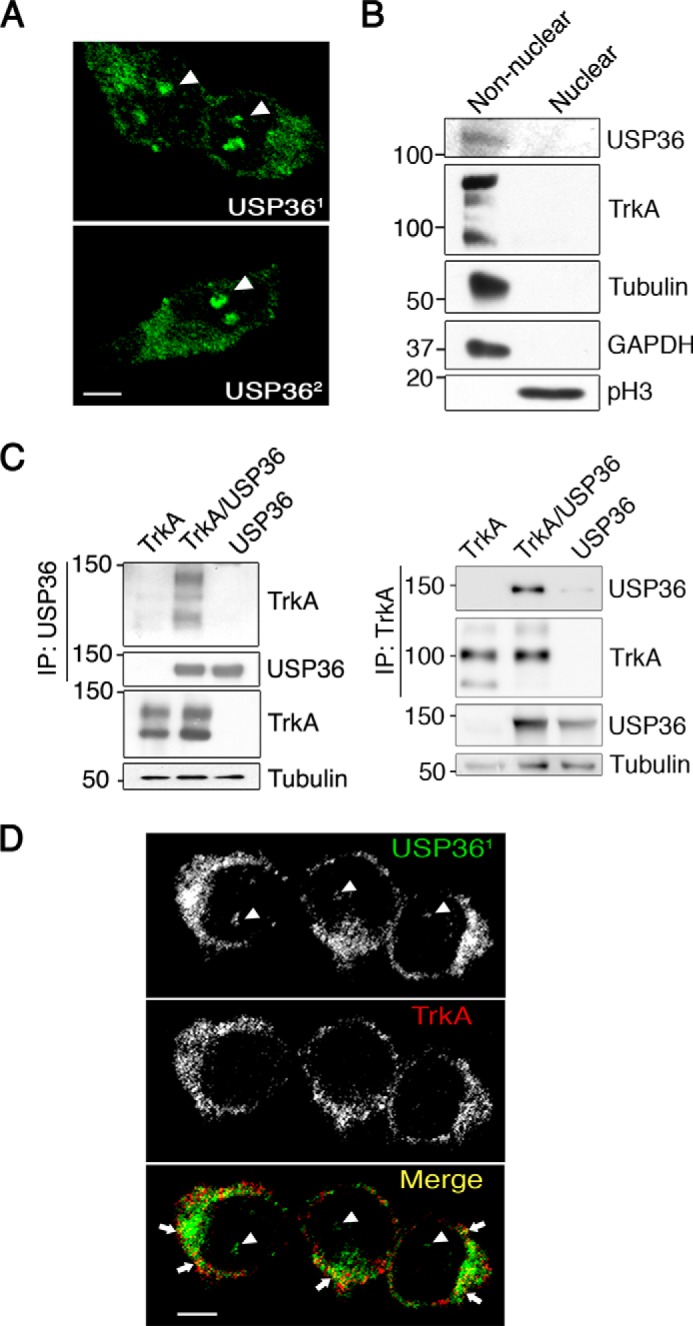
USP36 interacts and co-localizes with TrkA in PC12-6/15 cells. A, localization of USP36 in PC12-6/15 cells. USP36 immunofluorescence was detected using an antibody developed in our laboratory (top panel, USP361) and with an antibody obtained from Komada's laboratory (lower panel, USP362). Images were taken with a confocal microscope. Arrowheads indicate nucleoli staining. Scale bar, 5 μm. B, USP36 is mainly present in non-nuclear fractions in PC12-6/15 cells. Western blotting analyses were performed to detect USP36 in nuclear and non-nuclear fractions. TrkA, tubulin, and GAPDH were used as non-nuclear fractions, and phospho-Histone3 (pH3) was used as a nuclear marker. Note the presence of USP36 in non-nuclear fractions. C, USP36 interacts with TrkA. Lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with TrkA, FLAG-USP36, or TrkA and FLAG-USP36 were subjected to immunoprecipitation using FLAG antibodies (left panels) or TrkA antibodies (right panels). Western blotting was performed to assess co-immunoprecipitation of TrkA and USP36. The expression levels of TrkA, USP36, and tubulin as a loading control are shown. A representative experiment is shown (n = 3). D, co-localization of USP36 with TrkA. PC12-6/15 cells were seeded in coverslips, and immunofluorescence was performed using TrkA and USP36 antibodies. Images were taken with a confocal microscope. Arrows indicate co-localization of USP36 and TrkA, and arrowheads indicate nucleolar staining. Scale bar, 5 μm.
