FIGURE 4.
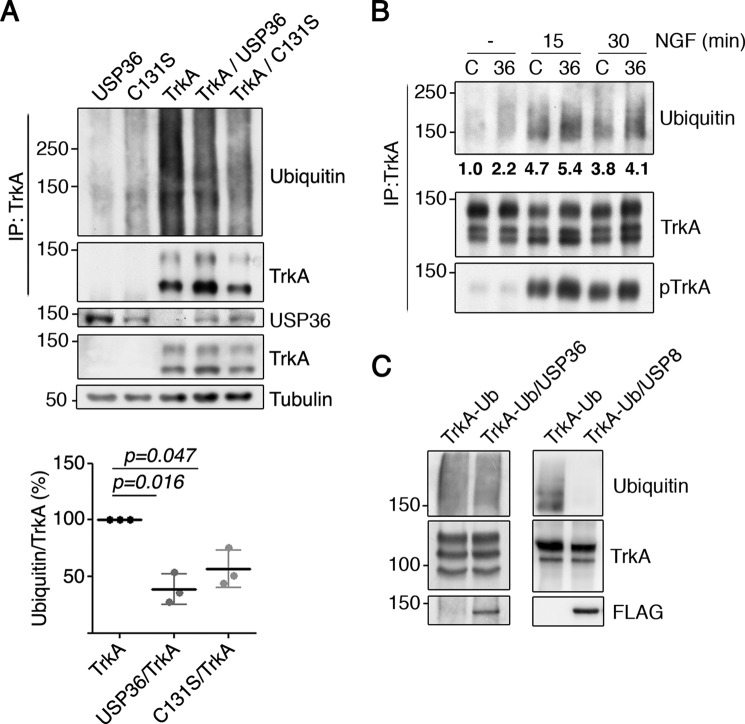
USP36 modulates TrkA ubiquitination in cells but not in vitro. A, TrkA ubiquitination is reduced in the presence of USP36 or USP36-C131S in HEK293 cells. Lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with different plasmids were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using TrkA antibodies. Western blotting was performed to assess TrkA ubiquitination in the presence or absence of USP36. The expression levels of FLAG-USP36, TrkA, and tubulin, as the loading control, are shown. Note the reduced ubiquitination when TrkA is expressed together with WT USP36 or mutant USP36-C131S. A representative experiment is shown. Quantification of TrkA ubiquitination levels (bottom panel) is shown (means ± S.D.; n = 3; two-tailed unpaired Student's t test). B, USP36 depletion increases TrkA ubiquitination in response to NGF. PC12-6/15 cells infected with lentiviruses expressing control shRNA (C) or USP36 shRNA-1 (36) were serum-starved overnight and then stimulated with NGF (100 ng/ml) for the corresponding time. Lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using TrkA antibodies and subjected to Western blotting analysis to detect TrkA ubiquitination, TrkA activation, and TrkA. A representative experiment is shown. Quantification of TrkA ubiquitination levels in the above blot is shown. C, USP36 does not deubiquitinate TrkA in vitro. Lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with TrkA or with FLAG-USP36 were subjected to immunoprecipitation using antibodies TrkA or FLAG antibodies, respectively. FLAG-USP36 was eluted from the antibodies using FLAG peptide and added to one of the tubes containing TrkA. An in vitro deubiquitination reaction was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” (left panels). As a positive control, in vitro deubiquitination assays were performed using FLAG-USP8 (right panels) using ubiquitinated TrkA from NGF-treated PC12-6/15 cells. A representative experiment for each DUB is shown (n = 3).