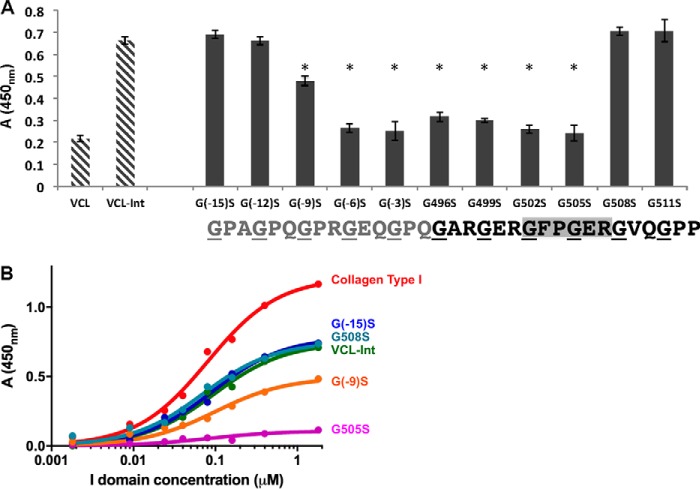
FIGURE 4.
A, solid-state analysis of recombinant α2 I domain binding to all recombinant bacterial collagens containing Gly to Ser substitutions at an I domain concentration of 0. 4 μm. The two striped columns on the left are the negative control VCL with no binding and the wild-type VCL-Int with strong binding. Experiments were carried out in triplicate, and error bars represent the standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed with the paired t test. Columns marked with an asterisk showed a statistically significant difference in binding compared with the VCL-Int control (p ≤ 0.01). B, dose response of I domain binding to recombinant collagens adsorbed onto 96-well plates. Bound protein was detected with antibodies and measured as absorbance at 450 nm. Red, collagen type I; green, VCL-Int; cyan, G508S; purple, G505S; orange, G(−9)S; blue, G(−15)S. Data were fit in GraphPad Prism® using a non-linear fit (one site, specific binding). Error bars are not included because only one set of experiments can be carried out on a given 96-well plate, and it is not possible to average values between different plates due to slight changes in conditions. All assays have been independently repeated at least three times on new plates to confirm that results are consistent.