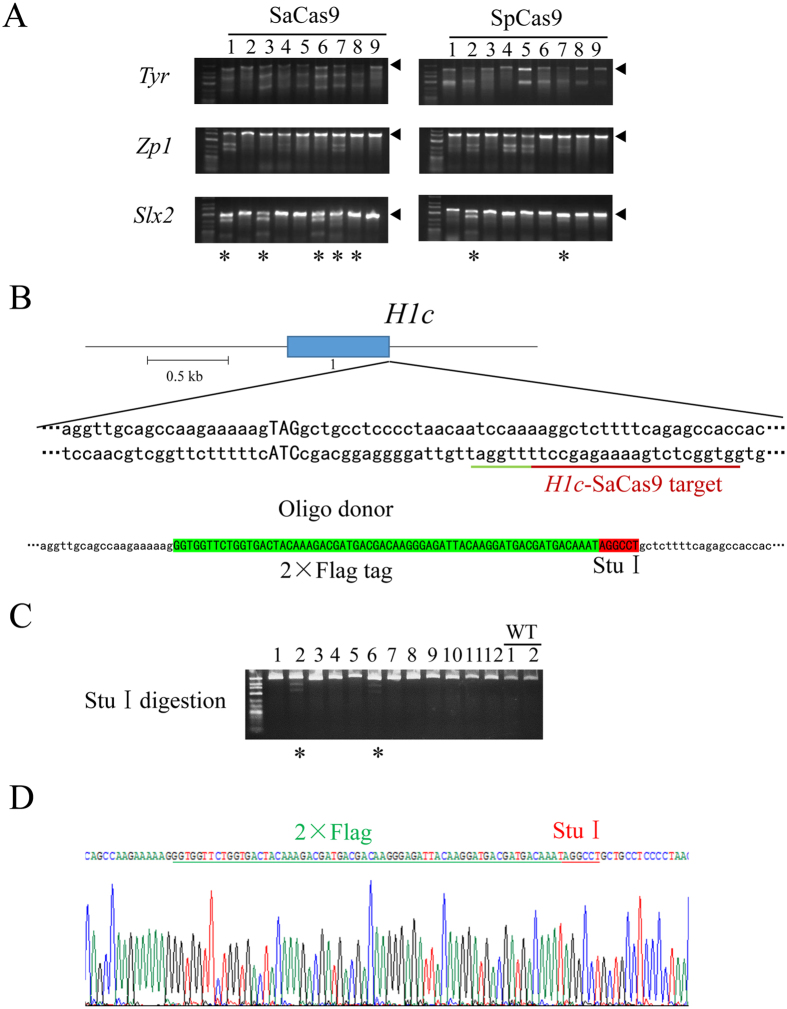
Figure 4. SaCas9-mediated multiplex gene disruption and homology directed repair (HDR) in mouse embryos.
(A) gRNAs targeting Tyr, Zp1, and Slx2 were simultaneously injected into mouse zygotes with their respective Cas9 mRNAs. Regions spanning the target sites were PCR amplified for T7EI analysis. Arrowheads indicate uncut (or no mismatch) PCR products. All embryos were further genotyped by Sanger sequencing. *Indicates triple targeted embryos. Sanger sequencing revealed that #2, #3, #6 and #8 embryos from Zp1 and #8 embryo from Slx2 (both in the SaCas9 group) had homozygous deletions. And Tyr and Zp1 from #8 embryos of SpCas9 group also had homozygous deletions. (B) The design of the gRNA and single-stranded DNA oligo for the H1c locus. The target site is underlined in red, and the PAM sequence in green. The 2 × Flag tag coding sequence is in green and StuI site in red. (C) The region encompassing the target site of the H1c locus was PCR amplified and then digested with StuI for RFLP (Restriction fragment length polymorphism) analysis. *Indicates embryos repaired by HDR. (D) PCR products from (C) were TA cloned for sequence verification of successful knock-in. A Representative sequencing chromatograph is shown. The 2 × Flag tag sequence and StuI site are underlined respectively in green and red.