Figure 3.
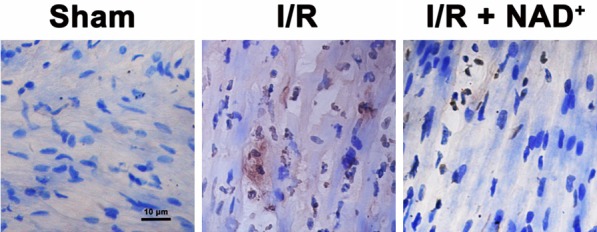
NAD+ administration attenuated myocardial I/R-induced increases in TUNEL signals in rat hearts. The rats were injected with saline or 20 mg/kg NAD+ intravenously. Subsequently, the rats were submitted to myocardial I/R surgery. Six hours after the reperfusion, the sections of rat hearts were stained for detecting TUNEL signals. NAD+ treatment markedly reduced the I/R-induced increases in TUNEL signals. N = 6.
