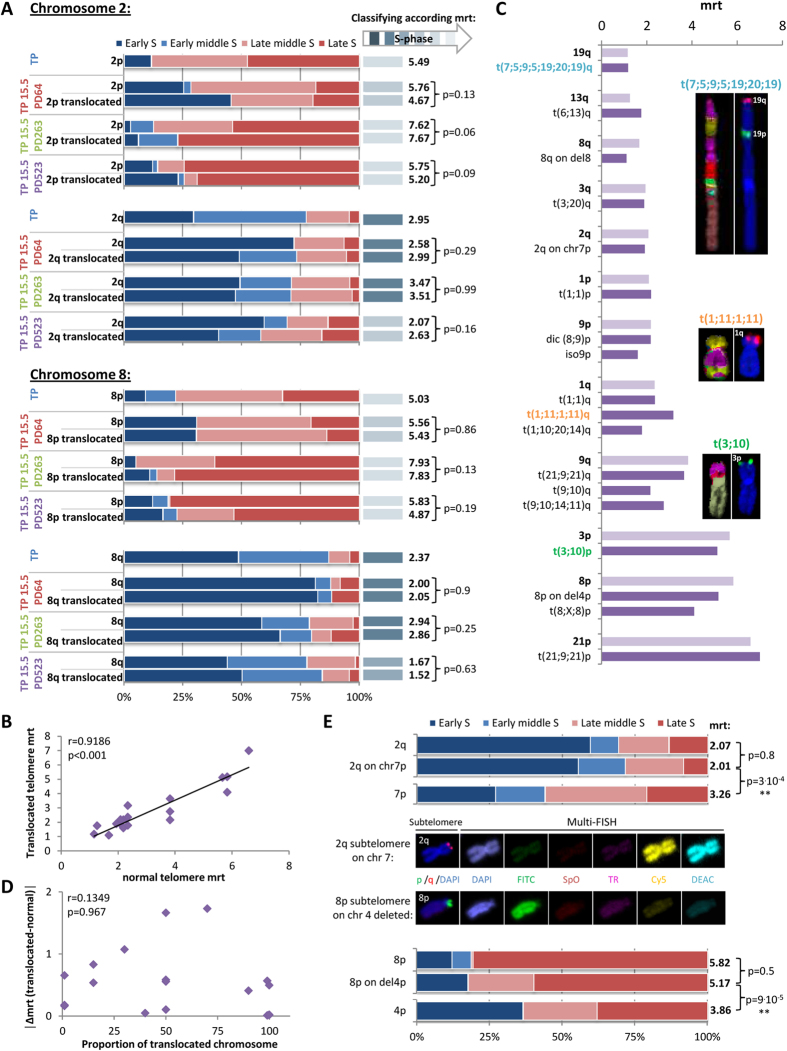
Figure 6. Translocated telomeres possessing their initial subtelomere retain their replication timing.
(A) Replication timing of telomeres of both arms of chromosomes 2 and 8 in all PD studied (i.e. TP as a control cell and PD64, PD263 and PD523 of TP15.5) for normal and rearranged chromosomes. Telomeres are classified according to their mrt (right). Translocated telomeres have the same replication timing as telomeres from normal chromosomes even if they temporarily change their replication timing in some PD (at PD64 for telomeres 2p and 8p, and at PD523 for telomeres 2q and 8q), (Fisher exact test). (B) Significant correlation between mrt of normal and translocated telomeres in TP15.5 PD523 (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient), indicating that telomere replication timing is not modified by the translocation of telomeres onto another chromosome. (C) Examples of the comparison of mrt of normal and translocated telomeres in PD523 of TP15.5. Telomeres are listed in ascending order by normal telomere mrt. t(7;5;9;5;19;20;19) and t(1;11;1;11) as a complex chromosomal rearrangement and t(3;10) as a simple chromosomal rearrangement are represented. Translocated telomeres (dark purple) appear to have generally the same replication timing as normal ones (light purple). (D) No correlation between the length of translocated arms and the difference of mrt between normal and translocated telomeres, indicating that the length of the translocated arm does not affect the mrt of the translocated telomeres (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient). (E) Comparisons of replication timing between a normal telomere and a telomere translocated only with its subtelomere in TP15.5 PD523: (i) telomere 2q, translocated telomere 2q on chromosome 7, and normal telomere 7p (upper panels), (ii) telomere 8p, translocated telomere 8p on chromosome 4 deleted and normal telomere 4p (lower panels). Images of these chromosomal rearrangements were captured (middle panels) by hybridization with subtelomere specific probes (p-arm in FITC and q-arm in TexasRed) and Multi-FISH (combination of Cy5 and DEAC label corresponds to chromosome 7, and a single label of FITC corresponds to chromosome 4). Telomeres translocated along with their subtelomeres onto another chromosome follow the replication timing of normal telomeres (Fisher exact test).