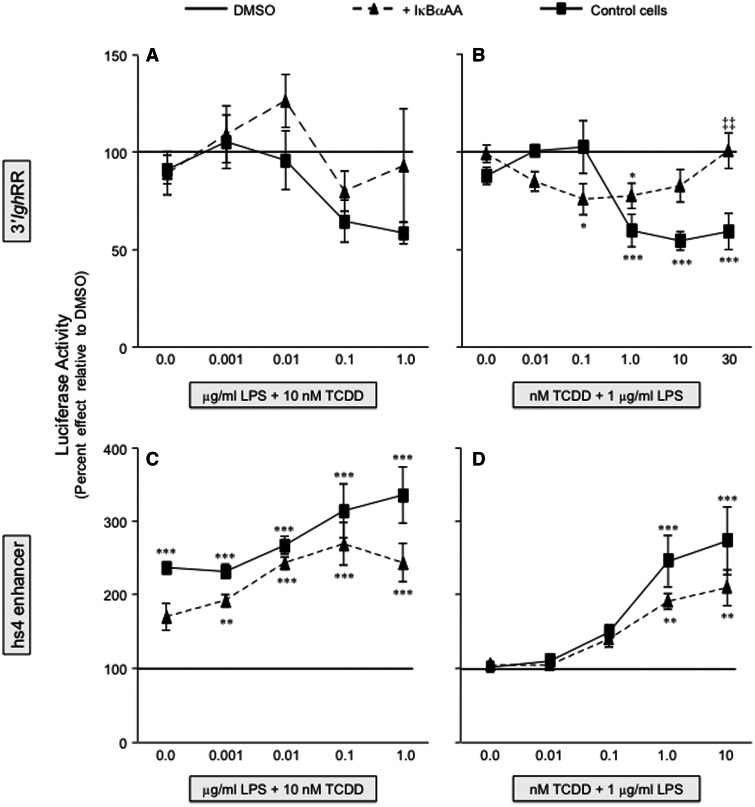
FIG. 5.
IκBαAA expression abrogates the inhibitory effect of TCDD on 3′IghRR activation and reduces the synergistic activation of hs4. The CH12.IκBαAA cells were transiently transfected with VH-Luc-3′IghRR (A and B) or VH-Luc-hs4 (C and D) and treated with either increasing concentrations of LPS (A and C) or increasing concentrations of TCDD (B and D). Luciferase enzyme activity (a single representative experiment is shown in Figs. 3 and 4) was normalized to percent effect relative to the appropriate DMSO vehicle control (represented by the line at 100%) and the mean from 3 separate experiments (n = 3–4 per treatment group) was averaged and represented on the y-axis as the overall mean ± SE. Statistical significance was determined by a 2-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni’s post hoc test. “*,” “**,” “***” denote significance at P < .05, P < .01, and P < .001, respectively, from the appropriate vehicle control (0.01% DMSO for [A] and [C]; 0.01% DMSO + 1 μg/ml LPS for [B] and [D]), which is represented by the line at 100%. “‡‡” denotes significance for a specific treatment at P < .01, respectively, between the control cells (no IκBαAA) and the cells induced to express the IκBαAA superrepressor (+ IκBαAA). Results are the overall average ± SE of 3 separate experiments.