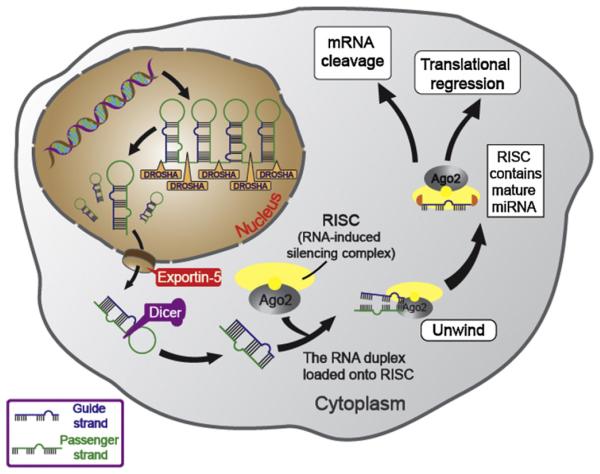
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the microRNA generation and silencing mechanisms. Hairpin-forming pre-miRNAs are generated by pri-miRNAs, which is cleaved by Drosha. Later, pre-miRNAs are transported into the cytoplasm by exportin-5 and further converted into double-stranded mature miRNAs by Dicer. Mature miRNAs are incorporated into the RISC complex, unwound and annealed to the target mRNAs carrying complementary sequences. miRNAs are able to regulate tens to hundreds of mRNAs via the imperfect base pairing between miRNAs and the 3′ or 5′ untranslated region of the target mRNAs. The miRNA-mRNA interaction silences the target genes through mRNA cleavage or translational inhibition.