Fig. 7.
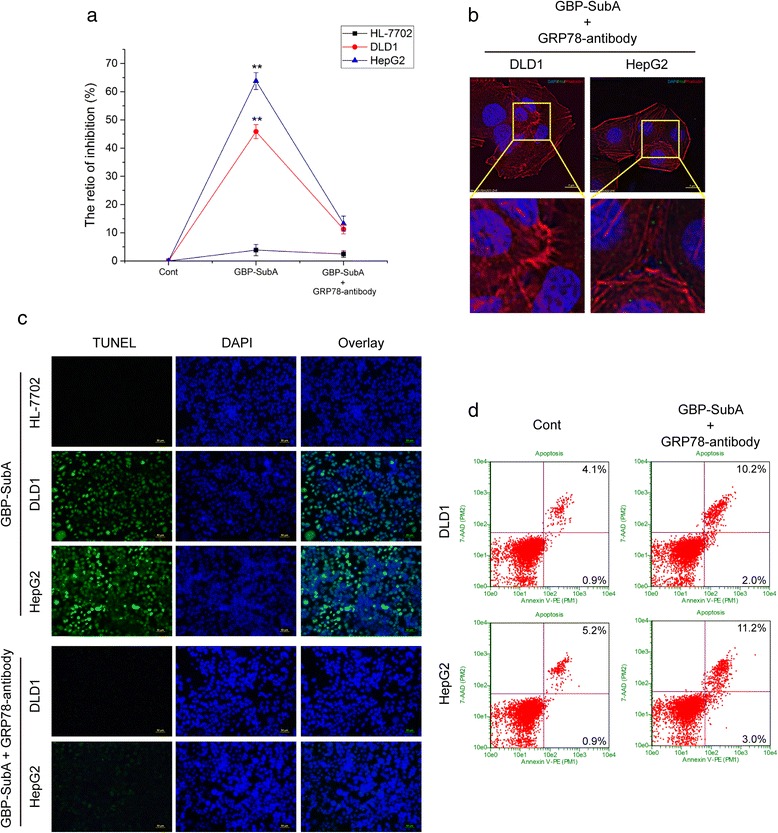
Verification of GBP-SubA bioactivity by blocking cell surface GRP78. a. After blocking cell surface GRP78, the cell inhibition ratios of GBP-SubA were determined by the MTT assay. HL-7702, DLD1 and HepG2 cells were incubated with or without anti-GRP78 antibody 1 h, and then 0.1 μg/mL GBP-SubA was added in the medium to incubate for another 48 h. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, compared with the control. b. After blocking cell surface GRP78, the cellular entry of GBP-SubA was detected by immunofluorescence. DLD1 and HepG2 cells were incubated with anti-GRP78 antibody 1 h, and 0.1 μg/mL GBP-SubA was then added in the medium to incubate for another 12 h. c. HL-7702, DLD1 and HepG2 cells were incubated with 0.1 μg/mL GBP-SubA for 48 h. For antibody blocking groups, the anti-GRP78 was added 1 h earlier. The nucleus morphology of apoptotic cells was observed by TUNEL and DAPI staining. d. After blocking cell surface GRP78, the apoptosis-induction effect of GBP-SubA was analyzed by flow cytometry. DLD1 and HepG2 cells were incubated with anti-GRP78 antibody 1 h, and 0.1 μg/mL GBP-SubA was then added in the medium to incubate for another 48 h. The control was without GBP-SubA and anti-GRP78 treatment
