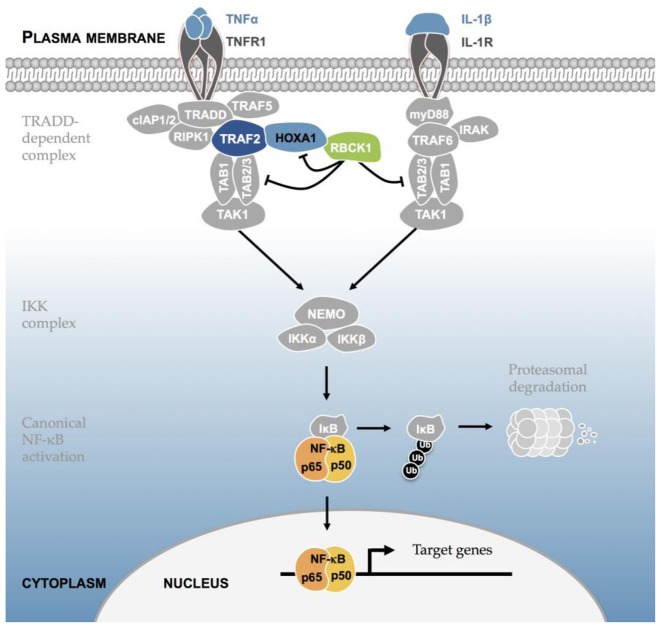
Figure 9.
Model for the HOXA1-mediated modulation of the NF-κB pathway. Upon TNF stimulation, TNFα binding to TNFR initiates the recruitment of TRADD that further recruits cIAP1/2, RIPK1, TRAF2 and TRAF5 to form the TRADD-dependent complex. This leads to the docking of TAK1 in complex with TAB2 and TAB3, allowing formation of the IKK complex. The IKK complex phosphorylates IκB, promoting its proteasomal degradation, allowing NF-κB release and finally its nuclear translocation to engage transcriptional programs. On the one hand, HOXA1 enhances TRAF2 activity or stabilizes the TRADD-dependent complex to activate the TNF/NF-κB pathway. On the other hand, RBCK1 inhibits HOXA1 as well as TAB2/3 to repress NF-κB activation. In addition, RBCK1 and TRAF2 can compete with each other to bind either the 11-His repeat or the homeodomain of HOXA1 (not represented).