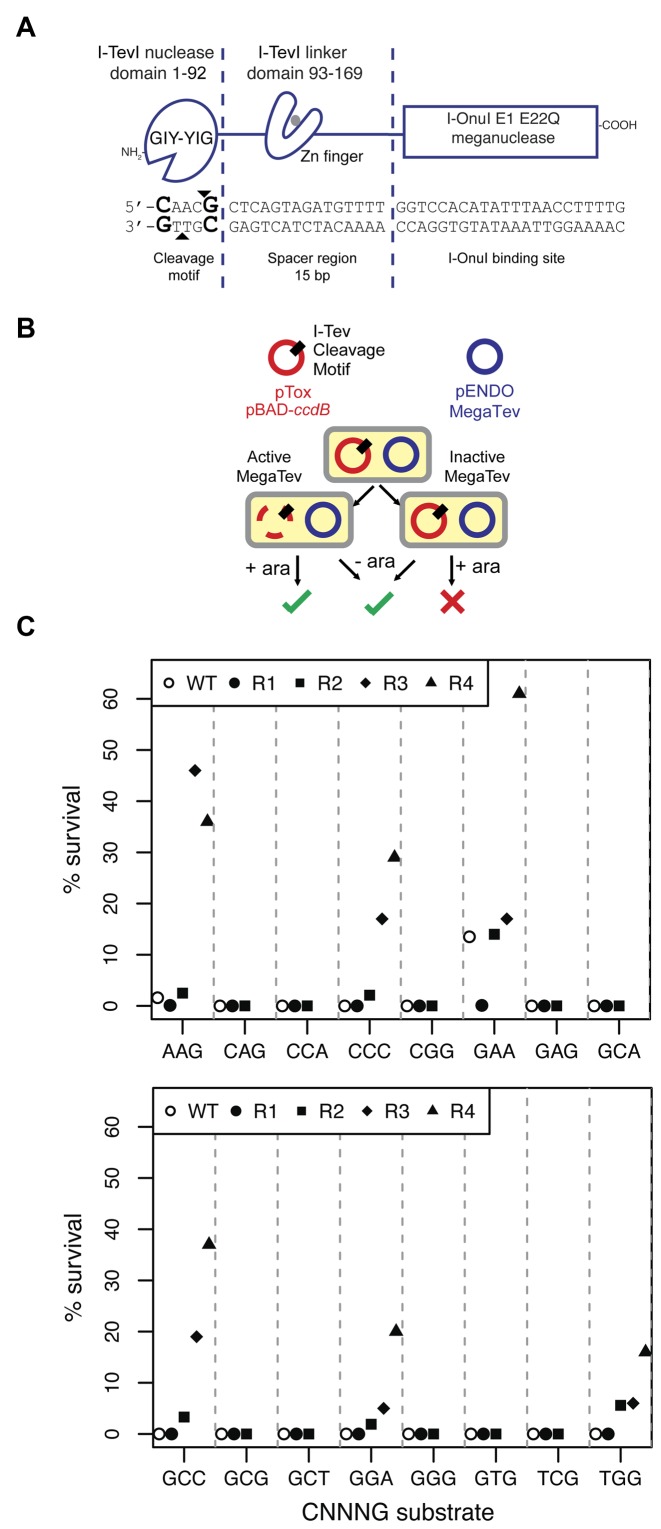
Figure 1.
Selection of I-TevI nuclease domain variants on cleavage site sequences non-permissive to the wild-type enzyme. (A) Schematic of the MegaTev endonuclease and DNA substrate. The individual domains of the MegaTev endonuclease are indicated, as are the corresponding regions of DNA substrate contacted by each domain. The I-TevI nuclease domain bottom- and top-strand nicking sites are indicated by black triangles, and the critical C1 and G5 positions of the cleavage site are in bold-type font. (B) The E. coli-based selection relies on a plasmid (pTox) carrying the ccdB gene that encodes a DNA gyrase toxin, and a MegaTev substrate. The MegaTev is expressed from a separate plasmid (pEndo). Selection outcomes with an active or inactive MegaTev when cells are plated on selective (+ara) or non-selective (-ara) media. (C) Results of initial screening and enrichment of 16 populations of MegaTev variants on the indicated CNNNG triplet substrates through four rounds of enrichment. Open circles indicate survival of the wild-type MegaTev (WT).