Figure 6.
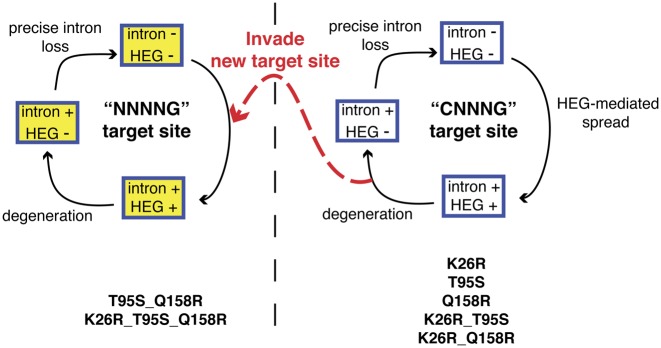
Escape and invasion of new target sites perpetuates the homing endonuclease life cycle. A modified schematic of the homing endonuclease life cycle depicts two populations of target sites, the CNNNG and NNNNG sites. Amino acid substitutions in the I-TevI nuclease domain that perpetuate maintenance and cycling through the CNNNG target site population are shown on the bottom right, while amino acid substitutions that facilitate invasion of the NNNNG target site population are shown on the bottom left.