Figure 8. Paxillin tyrosine phosphorylation is a prerequisite to paxillin phosphorylation on Ser273 by Pak .
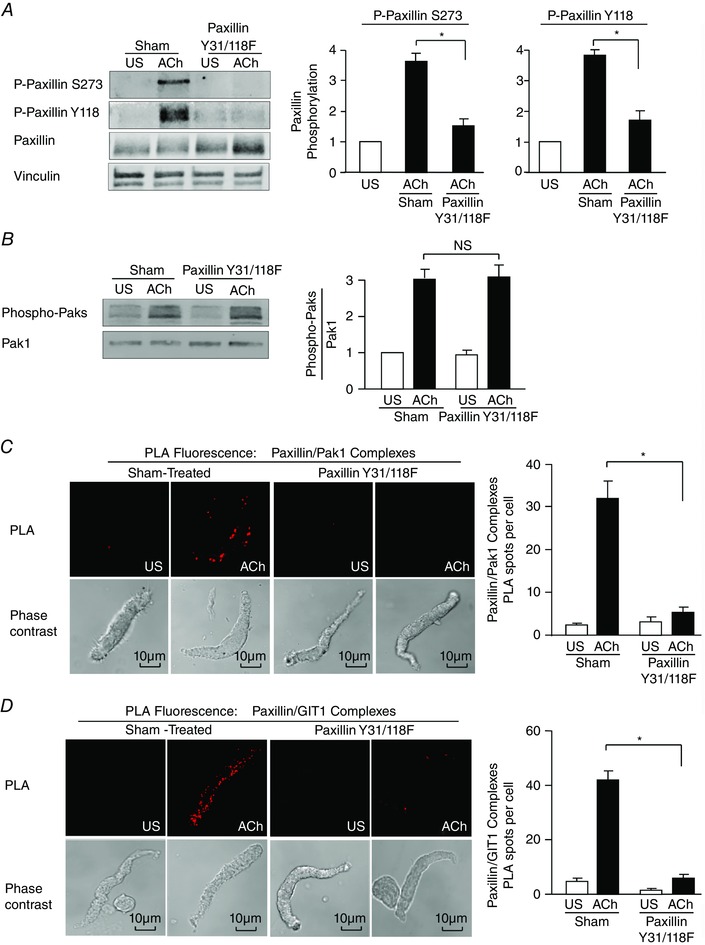
A, paxillin Tyr118 (Y118) phosphorylation and paxillin Ser273 (S273) were measured by immunoblot in extracts of tracheal smooth muscle tissues expressing the paxillin Y31/118F double mutant or sham‐treated tissues. Paxillin Y31/118F significantly inhibited ACh‐induced paxillin Tyr118 phosphorylation and also suppressed paxillin Ser273 phosphorylation (n = 4). B, expression of paxillin Y31/118F had no effect on ACh‐induced Pak activation as indicated by Thr423/Thr402 phosphorylation (n = 4). C, in situ PLA was used to analyse the interaction of paxillin and Pak1 in freshly dissociated differentiated canine tracheal smooth muscle cells. PLA fluorescence and phase contrast images are shown for each unstimulated (US) and ACh‐stimulated cell. In cells from sham‐treated tissues, the mean number of PLA spots was significantly higher in ACh‐stimulated cells than in unstimulated cells (n = 20 cells for ACh, n = 16 cells for US). In cells from paxillin Y31/118F‐treated tissues, the ACh‐induced increase in the mean number of PLA spots was very small and was significantly inhibited (n = 19 cells for ACh, n = 15 cells for US). Cells were dissociated from tissues obtained from three separate experiments. D, in situ PLA was used to analyse the interaction of paxillin and GIT1 in freshly dissociated differentiated canine tracheal smooth muscle cells. In cells from sham‐treated tissues, the mean number of PLA spots was significantly higher in ACh‐stimulated cells than in unstimulated cells (n = 30 cells for ACh, n = 13 cells for US). In cells from paxillin Y31/118F‐treated tissues, the ACh‐induced increase in the mean number of PLA spots was very small and was significantly inhibited (n = 21 for ACh, n = 13 for US). Cells were dissociated from tissues obtained from three separate experiments. Values are means ± SEM. *Significant difference between ACh‐stimulated tissues, P < 0.05. NS, not significantly different.
