Figure 10. Pak regulates the assembly of a multiprotein paxillin complex within smooth muscle cell adhesomes that mediates cdc42 and N‐WASP activation and actin polymerization .
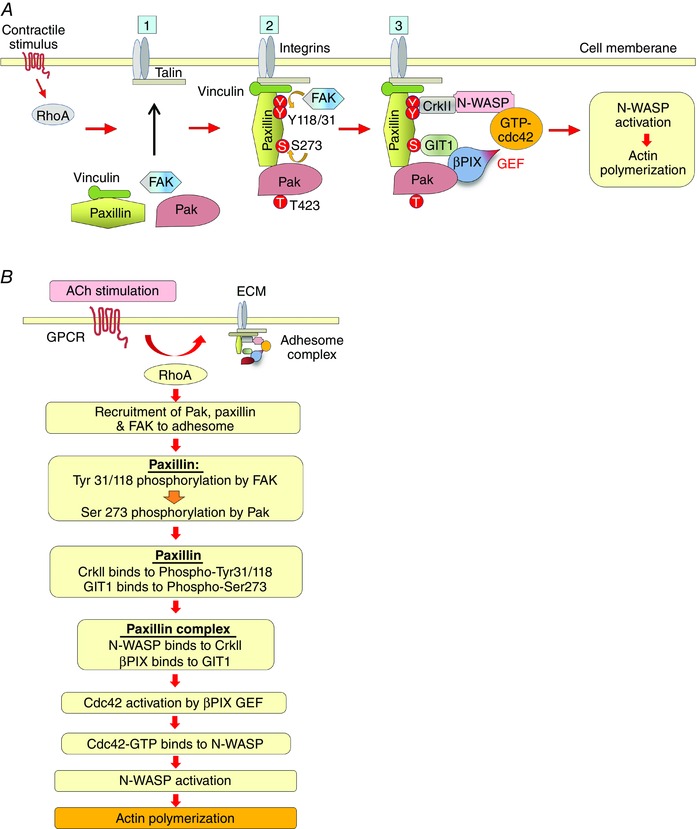
A, schematic diagram illustrating role of Pak in the assembly of a multiprotein paxillin complex that regulates actin polymerization at adhesion junctions in airway smooth muscle: ACh stimulation induces the recruitment of paxillin/vinculin complexes, FAK and Pak to adhesomes by a RhoA‐dependent mechanism. FAK then phosphorylates paxillin on Tyr 31 and Tyr118, facilitating the phosphorylation of paxillin on Ser273 by Pak. Paxillin 273 phosphorylation promotes its interaction with GIT1, and paxillin tyrosine phosphorylation regulates its interaction with the SH3/SH2 adaptor protein, CrkII. CrkII couples paxillin to N‐WASP and GIT1 couples paxillin to βPIX to form a paxillin complex that regulates the activation of cdc42 via the GEF activity of βPIX. cdc42 then catalyses the activation of N‐WASP and actin polymerization at the cortex of the smooth muscle cell. B, flow chart describing steps in the formation of the paxillin complex that regulates N‐WASP activation and actin polymerization within adhesion complexes in smooth muscle tissues. The polymerization of actin at the cortex of the cell and the fortification of the adhesome junctions facilitates the transmission of tension generated by contractile apparatus to the extracellular matrix when crossbridge cycling is activated by MLC phosphorylation (not shown).
