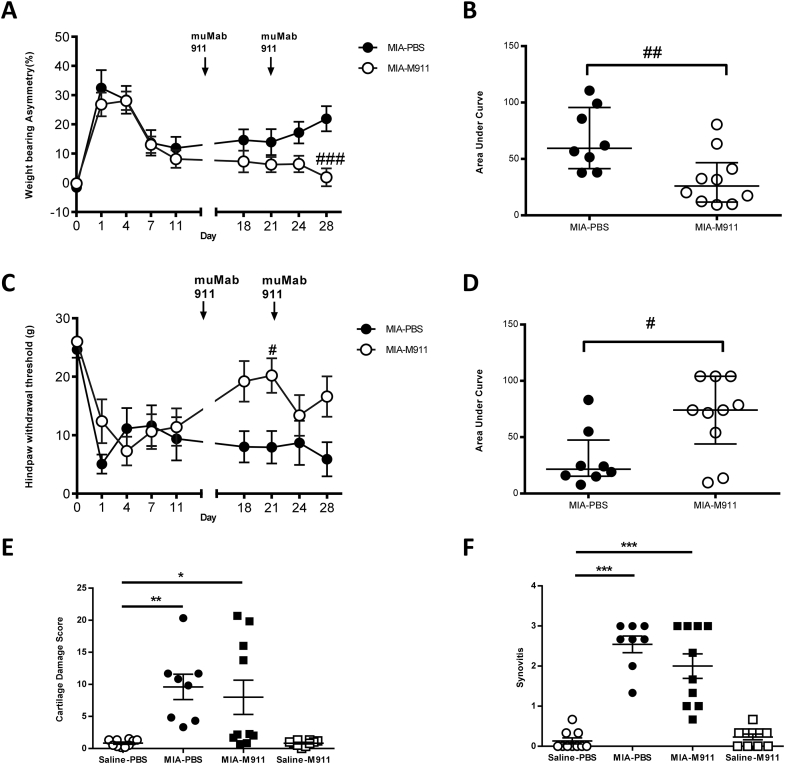
Fig. 4.
Therapeutic muMab 911 attenuates established OA pain behaviour but not cartilage damage and synovitis in the MIA model of OA pain. Rats received subcutaneous injection of 10 mg/kg muMab 911 or PBS on days 14 and 21 post intra-articular injection of MIA. muMab 911 treatment alleviated MIA-induced changes in weight-bearing asymmetry (A, B) and attenuated hindpaw withdrawal thresholds (C, D). Statistical comparison of muMab 911 and PBS treatment on pain behaviour, A, C are mean ± SEM (n = 8–10 rats per group): two-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post-hoc tests, #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001. Note behavioural data from rats which received intra-articular injection of saline were comparable to the preventative study, and are not shown for clarity. B, D are median and interquartile range, comparison of these data was performed with a Mann–Whitney U-test, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01. Therapeutic treatment with muMab 911 did not significantly alter MIA-induced cartilage damage (E) or synovial inflammation (F) (n = 8–10 rats per group). E, F are median and interquartile range, comparisons between groups used a Kruskal Wallis test with Dunn's post hoc comparison. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. M911: muMab 911.