Fig. 2. Antibiotics did not significantly increase conjugation efficiency.
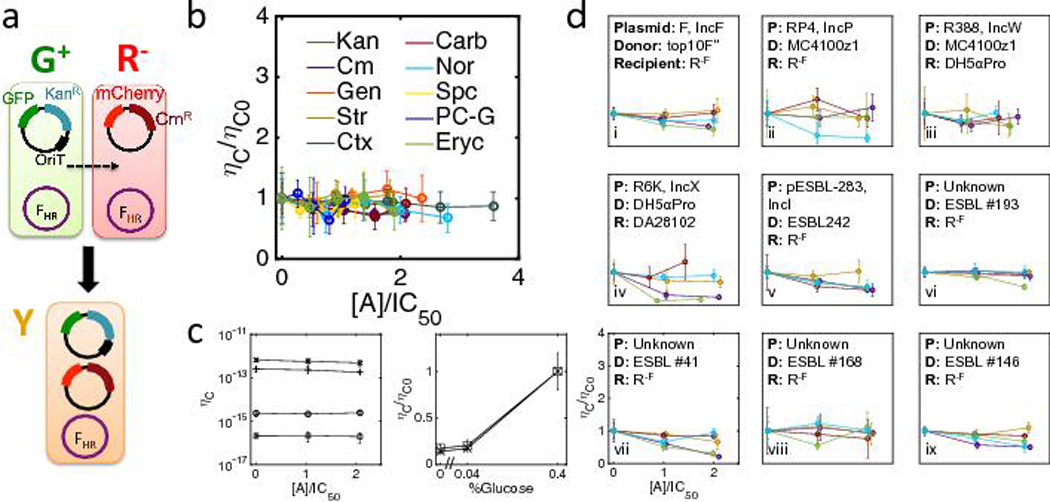
(a) A synthetic conjugation system (see Table S1). The recipient (R−) carries an immobile plasmid expressing cmR and an mCherry reporter. The donor (G+) carries a mobilizable plasmid expressing kanR and a GFP reporter. When mixed, G+ transfers a copy of its plasmid to R−, generating transconjugant Y. Transconjugants can be quantified by selective plating or by fluorescence imaging.
(b) Quantifying conjugation efficiency (ηC) for R− and G+ (see Table S2 and Methods for details) with 10 antibiotics. The y-axis is the conjugation efficiency normalized with the efficiency in the absence of antibiotics, ηC0 The x-axis is antibiotic concentration [A] normalized with each IC50 measured in plate readers (Fig. S2). There was no significant increase in ηC0 amongst all antibiotics and concentrations tested (P >0.15, one-tailed t-test, Table S3a). G− was mated with R− as control; no transconjugants were detected (CFU data not shown, demonstrated by Video S2).
(c) Left: Physiological state of the cells significantly influenced the conjugation efficiency. G+ and R−F cells were grown into exponential phase for 2 hours (See Methods). All four combinations of R−F and G+ from either stationary (s) or exponential (e) phase were tested, from top to bottom, Ge and Rs (crosses), Ge and Re (pluses), Gs and Rs (circles), and Gs and Re (squares). Str was used for these experiments, at concentrations of 0, 2, and 4 µg/mL. Differences in ηC between combinations are statistically significant (P<5×10−4, two-tailed t-test).
Right: Glucose significantly increases ηC. Crosses indicate without and boxes indicate with 2µg/mL Kan. Here, ηC0 is for the standard M9 conditions (glucose = 0.4%, Fig. 2b), since ηC under these conditions insignificantly changes between 0 and 2µg/mL Kan (P>0.71, one-tailed t-test).
(d) Antibiotics did not significantly increase the conjugation efficiency for five native self-transmissible conjugation systems, including F(i), RP4(ii), R388(iii), R6K(iv), and pESBL-283(v) from five incompatibility groups (IncF, IncP, IncW, IncX, and IncI), or for four ESBL-producing clinical E. coli isolates donors with unknown conjugation machinery (vi–ix) (P>0.15, one-tailed t-test. Donors and recipients are labeled in each panel (Table S1 and Methods).
Error bars for all data in Fig. 2 indicate mean ± standard deviation from four-six replicates.
