Abstract
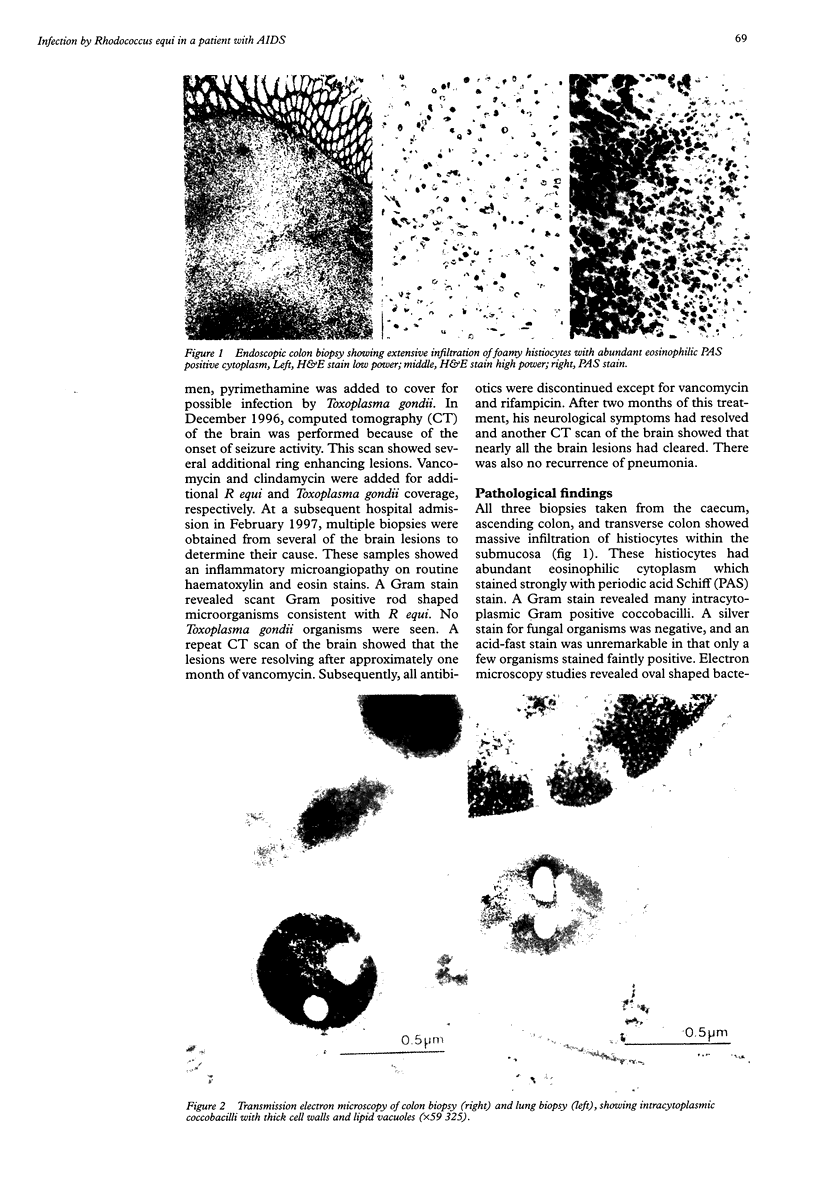
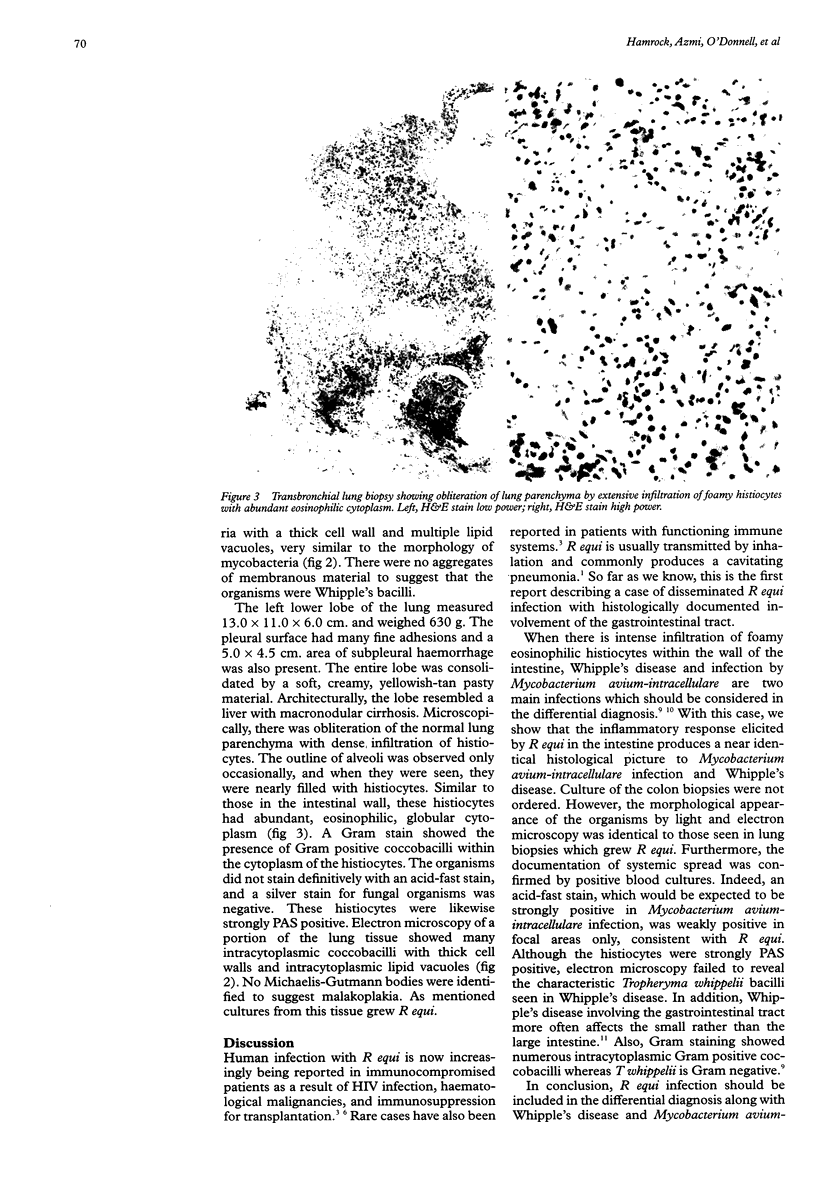
Rhodococcus equi pneumonia with systemic dissemination is being reported increasingly in immunocompromised patients. This is the first case report of disseminated R equi infection with biopsy documented involvement of the large intestine. The patient was a 46 year old male with AIDS who was diagnosed with cavitating pneumonia involving the left lower lobe. R equi was isolated in culture from the blood and lung biopsies. Subsequently, the patient developed anaemia, diarrhoea, and occult blood in the stool. Colonoscopy revealed several colonic polyps. Histological examination of the colon biopsies showed extensive submucosal histiocytic infiltration with numerous Gram positive coccobacilli and PAS positive material in the histiocytes. Electron microscopy showed variably shaped intrahistiocytic organisms which were morphologically consistent with R equi in the specimen. Disseminated R equi infection may involve the lower gastrointestinal tract and produce inflammatory polyps with foamy macrophages which histologically resemble those seen in Whipple's disease and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antinori S., Esposito R., Cernuschi M., Galli M., Galimberti L., Tocalli L., Moroni M. Disseminated Rhodococcus equi infection initially presenting as foot mycetoma in an HIV-positive patient. AIDS. 1992 Jul;6(7):740–742. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199207000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierer J., Wolf P., Seed L., Gay T., Noonan K., Haghighi P. Non-pulmonary Rhodococcus equi infections in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). J Clin Pathol. 1987 May;40(5):556–558. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.5.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame B. C., Petkus A. F. Rhodococcus equi pneumonia: case report and literature review. Ann Pharmacother. 1993 Nov;27(11):1340–1342. doi: 10.1177/106002809302701105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin D. B., Jr, Yium J. J., Hawkins S. S. Corynebacterium equi peritonitis in a patient receiving peritoneal dialysis. South Med J. 1989 Aug;82(8):1046–1047. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198908000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poorman J. C., Katon R. M. Small bowel involvement by Mycobacterium avium complex in a patient with AIDS: endoscopic, histologic, and radiographic similarities to Whipple's disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994 Nov-Dec;40(6):753–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F. Epidemiology of Rhodococcus equi infection in horses. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Aug;14(3):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. A., Graham B. S., Verrall R., Dixon R., Schaffner W., Tham K. T. Rhodococcus equi--an increasingly recognized opportunistic pathogen. Report of 12 cases and review of 65 cases in the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995 May;103(5):649–655. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/103.5.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Herbay A., Maiwald M., Ditton H. J., Otto H. F. Histology of intestinal Whipple's disease revisited. A study of 48 patients. Virchows Arch. 1996 Dec;429(6):335–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00198437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]